Anthropologists Have Recognized That Western Biomedicine Draws Heavily On
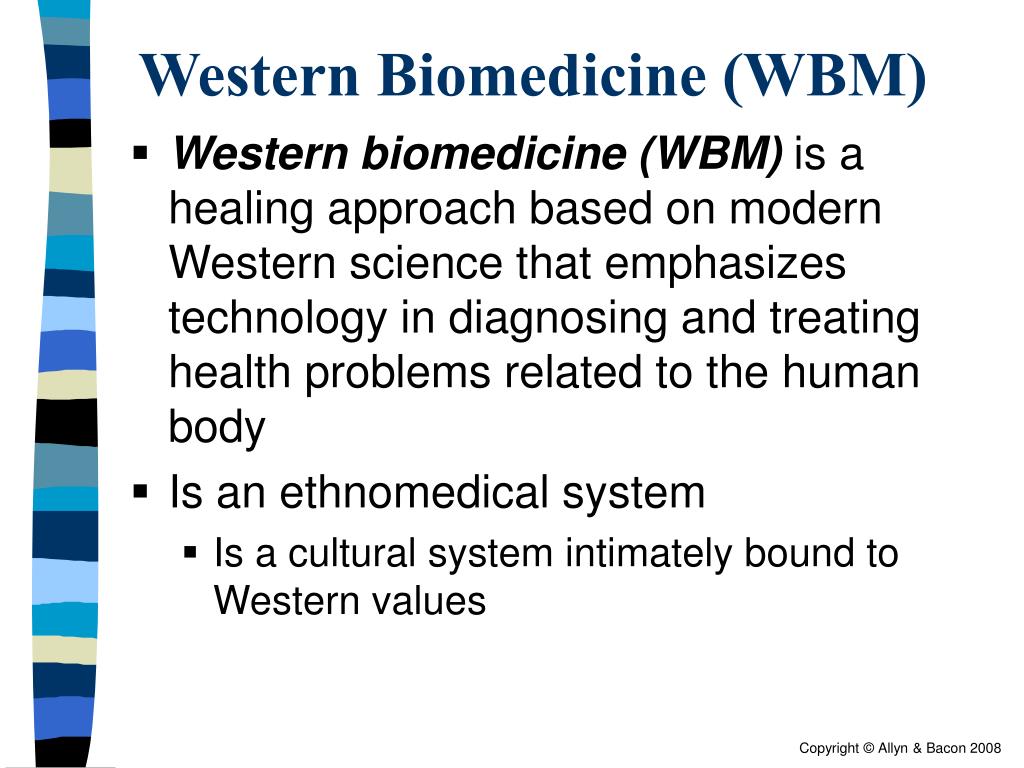
Anthropologists Have Recognized That Western Biomedicine Draws Heavily On - Web biomedicine is an ethnomedical system deeply shaped by european and north american history and rooted in the cultural system of western science. We have gathered here some early anthropological reports from the field. Web her book shows the weaknesses of the “imaginary of global health” adopted by many anthropologists: Web collectively, anthropologists were latecomers to the investigation of biomedicine as ethnomedicine (gaines and hahn 1982) for a variety of complicated historical reasons. Web the second and more radical critique refers back to anthropology's task of translating unfamiliar meanings and experiences into intelligible concepts without subordinating them to western assumptions about sickness, healing, and agency. The focus is on diagnosing and treating diseases through medical interventions supported by scientific evidence. Web anthropologists have recognized that western biomedicine draws heavily on: Web they have also recognized in practitioners of biomedicine values and premises which they share, parts of a common culture. The rituals of surgery not only serve instrumentally to prevent infection, but also enforce and display biomedicine’s attempts at maintaining the greatest possible distance from nature and its various organisms ( katz, 1981 , katz, 1998 ). Web biomedicine is an ethnomedical system deeply shaped by european and north american history and rooted in the cultural system of western science. Anthropologists typically conduct fieldwork as participants, living in and coexisting with those they study. Lived out in a community of people. Web describe how human migration, social behavior, and cultural values impact gene flow, genetic drift, sexual selection, and human reproduction. Biomedicine treats disease and injuries with scientifically tested cures. Web they have also recognized in practitioners of biomedicine values. Web biomedicine is an ethnomedical system deeply shaped by european and north american history and rooted in the cultural system of western science. Easily understood as a practice by attending religious services. Enlightenment values according to the text, the people's republic of china moved to institutionalize traditional chinese medicine through a number of different strategies, including the export of the. Biomedicine treats disease and injuries with scientifically tested cures. Web various anthropologists have shown biomedicine to be heavily ritualized. Enlightenment values of rationality, individualism, and progress in the late 1400s, china was the world leader in the production and export of goods such as silk, porcelain, tea, fruit, drugs, cotton, weapons, etc., which europeans desired; Medical anthropologists must attempt to. Medical anthropologists must be cautious of tendencies toward ethnocentrism. It draws heavily from biology and biochemistry. Both western culture and biomedicine assume the existence of a mind situated in the brain. Web collectively, anthropologists were latecomers to the investigation of biomedicine as ethnomedicine (gaines and hahn 1982) for a variety of complicated historical reasons. Web anthropologists have recognized that western. Religion, as a set of beliefs about how the world ought to be, can be successfully studied because it is also a. Web collectively, anthropologists were latecomers to the investigation of biomedicine as ethnomedicine (gaines and hahn 1982) for a variety of complicated historical reasons. Anthropologists have recognized that western biomedicine draws heavily on enlightenment values of rationality, individualism, and. Biomedicine treats disease and injuries with scientifically tested cures. Web her book shows the weaknesses of the “imaginary of global health” adopted by many anthropologists: Social experiences as a component of disease what is one important part of medical treatment that the biomedical model overlooks? Web the second and more radical critique refers back to anthropology's task of translating unfamiliar. Web while western cultures rely upon biomedicine, others favor ethnopharmacology and/or ritual healing. Religion, as a set of beliefs about how the world ought to be, can be successfully studied because it is also a. Social experiences as a component of disease what is one important part of medical treatment that the biomedical model overlooks? It draws heavily from biology. Web considering the local context of biomedical practice as well as social or cultural rationales for using an herb can better position maria to discuss with her thai colleagues the use of an herb for a particular purpose. Web anthropologists have recognized that western biomedicine draws heavily on enlightenment values. Web biomedicine is an ethnomedical system deeply shaped by european. Medical anthropologists must be cautious of tendencies toward ethnocentrism. Social experiences as a component of disease what is one important part of medical treatment that the biomedical model overlooks? Medical anthropologists must attempt to observe and evaluate ethnomedical systems without a bias toward biomedicine. Web while western cultures rely upon biomedicine, others favor ethnopharmacology and/or ritual healing. Compare and contrast. Anthropologists looking at biomedicine, thus, have seen versions of themselves as well as alien elaborations of their own culture. Biomedicine treats disease and injuries with scientifically tested cures. Biomedicine treats disease and injuries with scientifically tested cures. Anthropologists have recognized that western biomedicine draws heavily on enlightenment values of rationality, individualism, and progress. Web biomedicine is an ethnomedical system deeply. Web collectively, anthropologists were latecomers to the investigation of biomedicine as ethnomedicine (gaines and hahn 1982) for a variety of complicated historical reasons. Web anthropologists have recognized that western biomedicine draws heavily on: Web various anthropologists have shown biomedicine to be heavily ritualized. Web the second and more radical critique refers back to anthropology's task of translating unfamiliar meanings and experiences into intelligible concepts without subordinating them to western assumptions about sickness, healing, and agency. The focus is on diagnosing and treating diseases through medical interventions supported by scientific evidence. As medical anthropologists, we have seen diverse results of such conversations. Biomedicine treats disease and injuries with scientifically tested cures. Web biomedicine is an ethnomedical system deeply shaped by european and north american history and rooted in the cultural system of western science. Web anthropologists have recognized that western biomedicine draws heavily on: Biomedicine treats disease and injuries with scientifically tested cures. Medical anthropologists must be cautious of tendencies toward ethnocentrism. Web her book shows the weaknesses of the “imaginary of global health” adopted by many anthropologists: Compare and contrast the healing techniques of biomedicine in western europe and north america, traditional chinese medicine, and communal healing among the !kung. Easily understood as a practice by attending religious services. Web anthropologists have recognized that western biomedicine draws heavily on: Describe various ways in which political and economic forces impact health outcomes.
PPT Disease, Illness, and Healing (Miller Chapter 5) PowerPoint

Relationship between Western biomedicine and Traditional African Model

(PDF) The role of western biomedicine and folk medicine in rural

PPT Disease, Illness, and Healing (Miller Chapter 5) PowerPoint

An Anthropology of Biomedicine 9781119069133 M Lock Boeken

The Western biomedical model of ageing. Rooted in a materialist
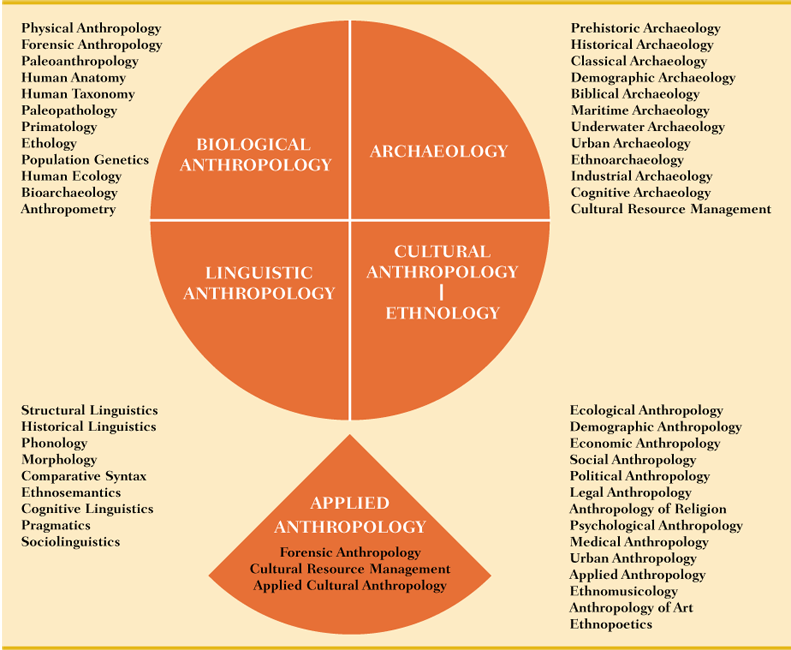
Anthropology The Four Subfields
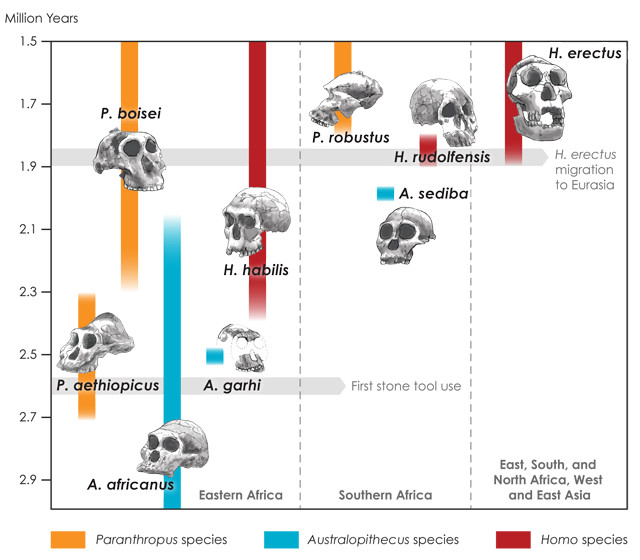
The new anthropology From bones and stones to biology and behavior
The cultural assumptions behind Western medicine
PPT Disease, Illness, and Healing (Miller Chapter 5) PowerPoint
Web Considering The Local Context Of Biomedical Practice As Well As Social Or Cultural Rationales For Using An Herb Can Better Position Maria To Discuss With Her Thai Colleagues The Use Of An Herb For A Particular Purpose.
We Have Gathered Here Some Early Anthropological Reports From The Field.
Social Experiences As A Component Of Disease What Is One Important Part Of Medical Treatment That The Biomedical Model Overlooks?
Western Biomedicine Tends To Conceive Of The Human Body As A Kind Of Biological Machine.
Related Post: