Cardiac Muscle Cells Drawing
Cardiac Muscle Cells Drawing - Their overlapping arrangements creates alternating dark (a) and light (i) bands or striations, similar to those seen in skeletal muscle tissue. Myocardial contractile cells and myocardial conducting cells. The myocardial contractile cells constitute the bulk (99 percent) of the cells in the atria and ventricles. Web why cardiomyocytes are important? Describe the structure of cardiac muscle. The fibers are separated by collagenous tissue that supports the capillary network of cardiac tissue. Within the mediastinum, the heart is separated from the other mediastinal structures by a tough membrane known as the pericardium. It is responsible for keeping. How many cardiomyocytes are in the human heart? Now, i will provide the cardiac muscle. The human heart is located within the thoracic cavity, medially between the lungs in the space known as the mediastinum. Web cardiac muscle under microscope 40x, 100x, and 400x. Web the individual cardiac muscle cells are arranged in bundles that form a spiral pattern in the wall of the heart. Web this can be seen in the image below. The. The myofibrils consist of repeating sections of sarcomeres, which are the fundamental contractile units of the muscle cells. Today, in this short article, i will show you the important histological features from the cardiac muscle histology slide. The human body quiz cardiac muscle cells form a highly branched cellular network in the heart. Web cardiac muscle tissue, or myocardium, is. Web there are two major types of cardiac muscle cells: Now, i will provide the cardiac muscle. What are the three different types of muscles in the human body? Their overlapping arrangements creates alternating dark (a) and light (i) bands or striations, similar to those seen in skeletal muscle tissue. Compare the effect of ion movement on membrane potential of. Identify and describe the components of the conducting system that distributes electrical impulses through the heart. Web cardiac muscle under microscope 40x, 100x, and 400x. What are the three different types of muscles in the human body? The fibers are separated by collagenous tissue that supports the capillary network of cardiac tissue. Where two cells meet a specialized junction called. Now, i will provide the cardiac muscle. Web location of the heart. Web they act as a storehouse for calcium. Web cellular level cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) are striated, branched, contain many mitochondria, and are under involuntary control. Web 1 2 thick and thin myofilaments are present and organized into myofibrils. The fibers are separated by collagenous tissue that supports the capillary network of cardiac tissue. Diagrammatic view of three types. Web there are two major types of cardiac muscle cells: It is the pen diagram of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle for class 10, 11 and 12. Web also known as myocardiocytes, cardiomyocytes are cells that make up the heart. The myocardial contractile cells constitute the bulk (99 percent) of the cells in the atria and ventricles. List of the difference between three muscle cell types what are the special features of cardiomyocytes? Each myocyte contains a single, centrally located nucleus surrounded by a cell membrane known as the sarcolemma. Web they act as a storehouse for calcium. Web why. List of the difference between three muscle cell types what are the special features of cardiomyocytes? Web britannica quiz facts you should know: Figure 19.2 shows the position of the heart within the thoracic cavity. Web cellular level cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) are striated, branched, contain many mitochondria, and are under involuntary control. Web cardiac muscle histology and slide identification. Cardiac muscle tissue contracts and releases involuntarily. The myocardial contractile cells constitute the bulk (99 percent) of the cells in the atria and ventricles. Web they act as a storehouse for calcium. The myofilaments of cardiac muscle are arranged in a similar pattern to skeletal muscle, resulting in cross. Diagrammatic view of three types. List of the difference between three muscle cell types what are the special features of cardiomyocytes? Web cardiac muscle under microscope 40x, 100x, and 400x. Web cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle tissues, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle.it is an involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes. Web cellular level cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) are striated, branched, contain many mitochondria, and are under involuntary control. In human beings, as well as many other animals, cardiomyocytes are the first. The myofilaments of cardiac muscle are arranged in a similar pattern to skeletal muscle, resulting in cross. The myocardial contractile cells constitute the bulk (99 percent) of the cells in the atria and ventricles. Now, i will provide the cardiac muscle. Figure 19.2 shows the position of the heart within the thoracic cavity. It is the pen diagram of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle for class 10, 11 and 12. List of the difference between three muscle cell types what are the special features of cardiomyocytes? They are connected end to end by intercalated disks and are organized into layers of myocardial tissue that are wrapped around the chambers of the heart. Cardiac muscle tissue contracts and releases involuntarily. Web britannica quiz facts you should know: Web cardiac muscle histology and slide identification points. Web why cardiomyocytes are important? The cytoplasmic continuity present between the neighbouring cells is called the syncytium. The myocardial contractile cells constitute the bulk (99 percent) of the cells in the atria and ventricles. Myocardial contractile cells and myocardial conducting cells.
cardiac muscle Definition, Function, & Structure Britannica
Illustration of the human cardiac muscle cells on a white background
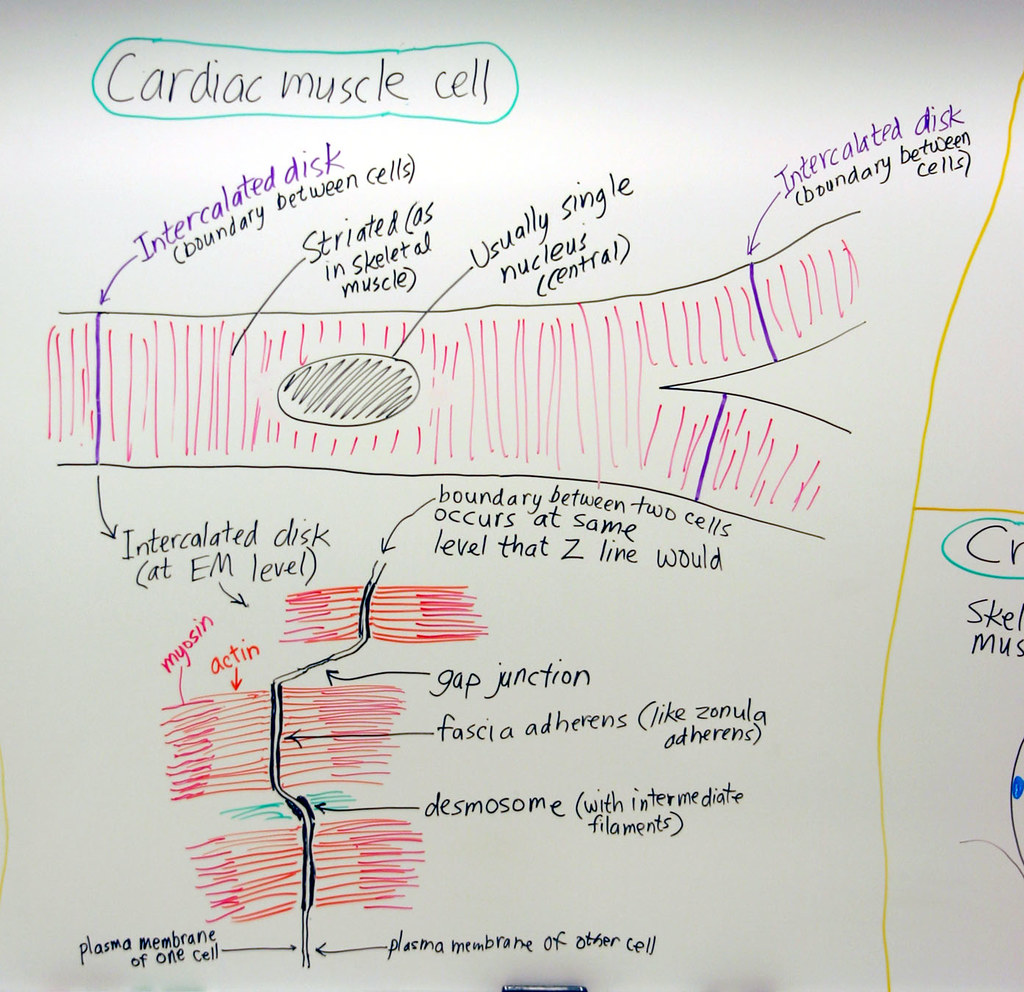
Muscle Cardiac Muscle Cell A hand drawn sketch by Dr. Chr… Flickr
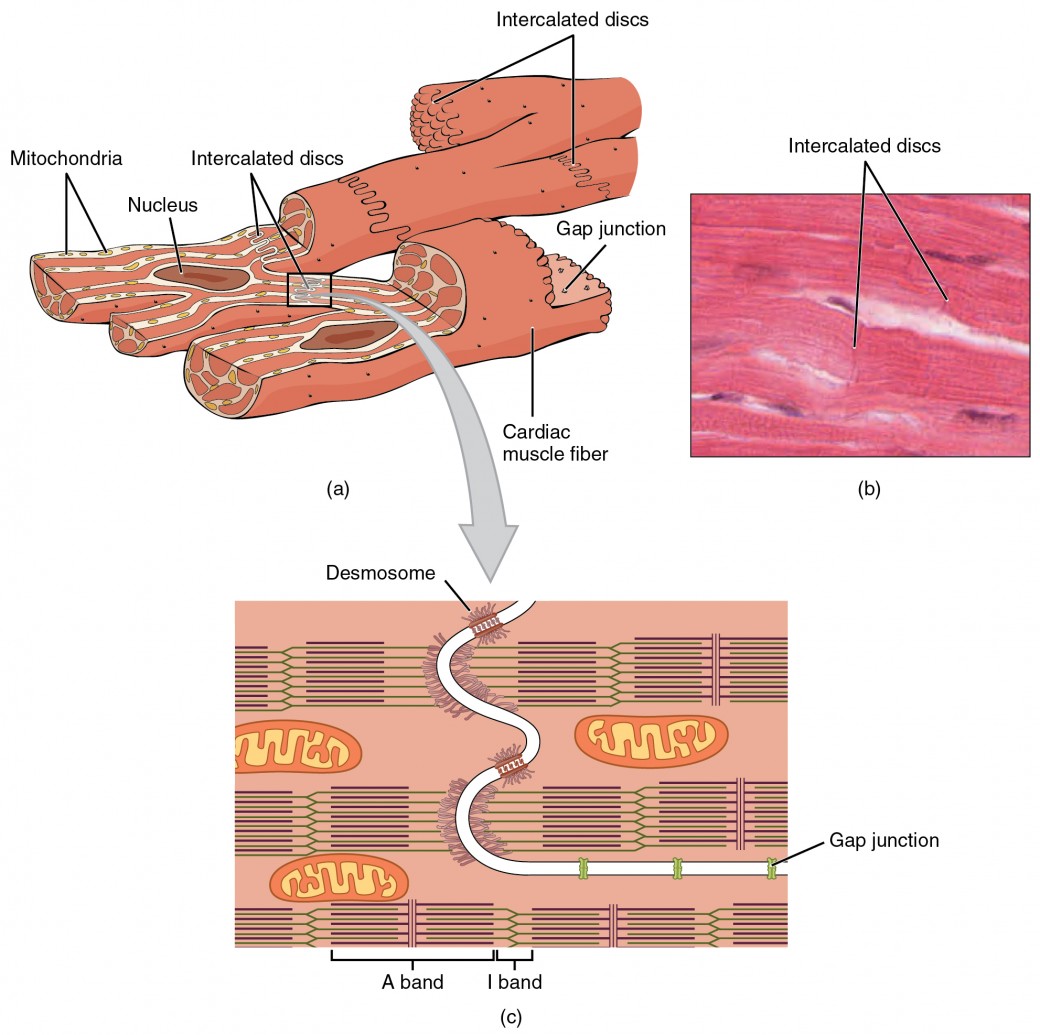
Cardiac Muscle and Electrical Activity Anatomy and Physiology II

Structure of Cardiac Muscle Fibers. Anatomy of Cardiomyocyte Stock
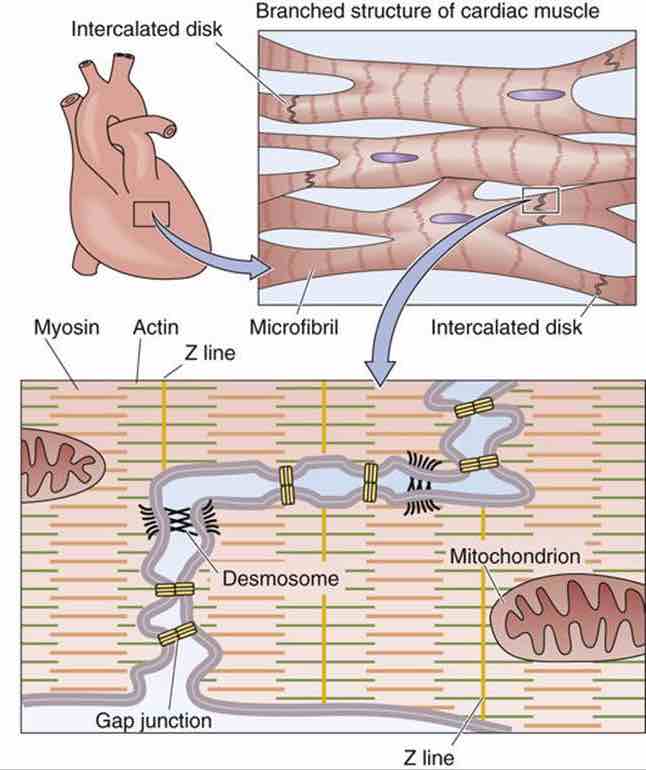
Cardiomyocytes (Cardiac Muscle Cells) Structure, Function, Cell

Cardiac Muscle Definition, Function and Structure Biology Dictionary

Heart Anatomy · Anatomy and Physiology
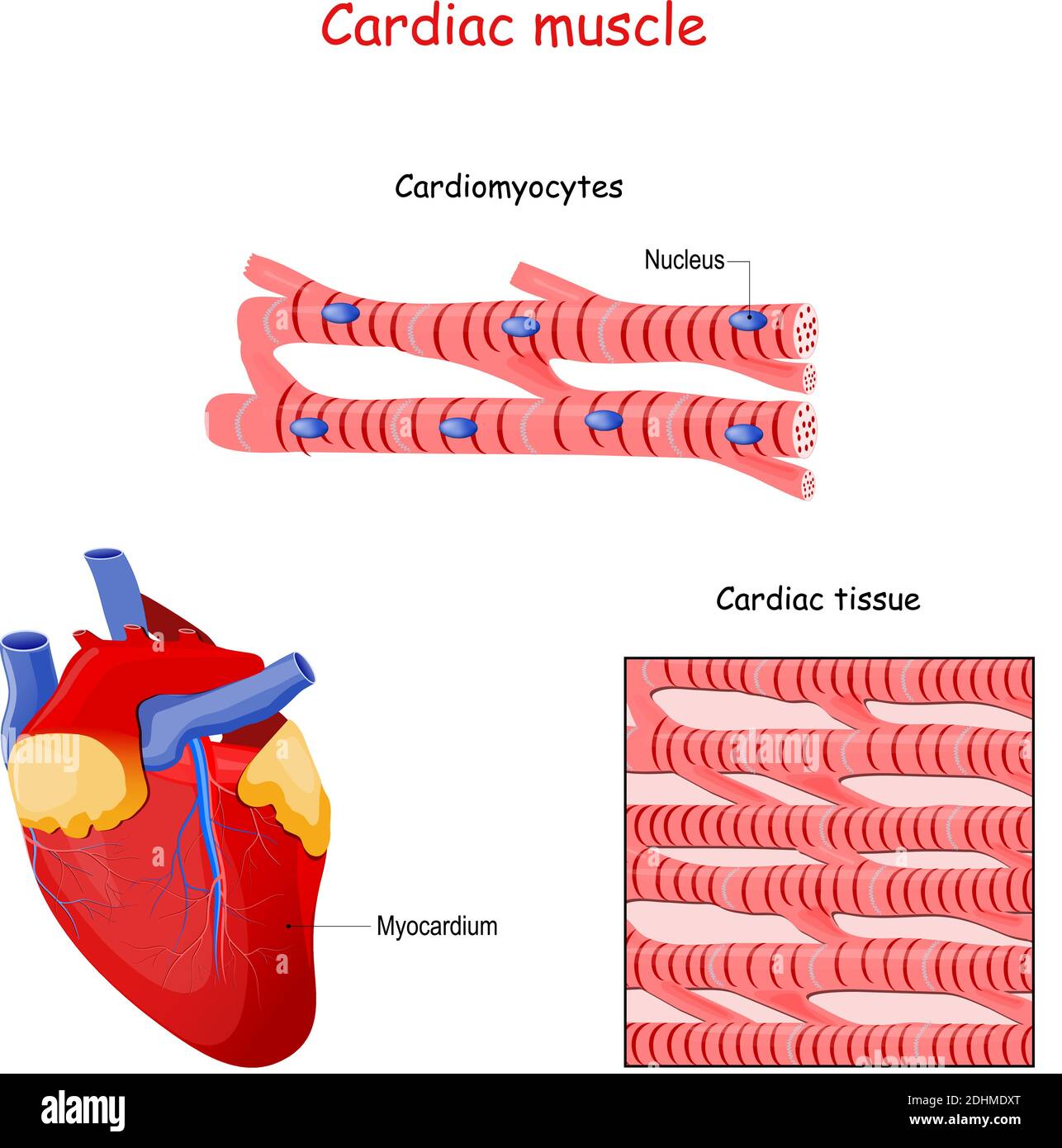
Structure of Cardiac muscle fibers. anatomy of cardiomyocyte
Cardiac Muscle Cells
Web They Act As A Storehouse For Calcium.
Web About 1% Of The Cardiac Muscle Cells In The Heart Are Responsible For Forming The Conduction System That Sets The Pace For The Rest Of The Cardiac Muscle Cells.
Compare The Effect Of Ion Movement On Membrane Potential Of Cardiac Conductive And Contractile Cells.
What Are The Three Different Types Of Muscles In The Human Body?
Related Post:
