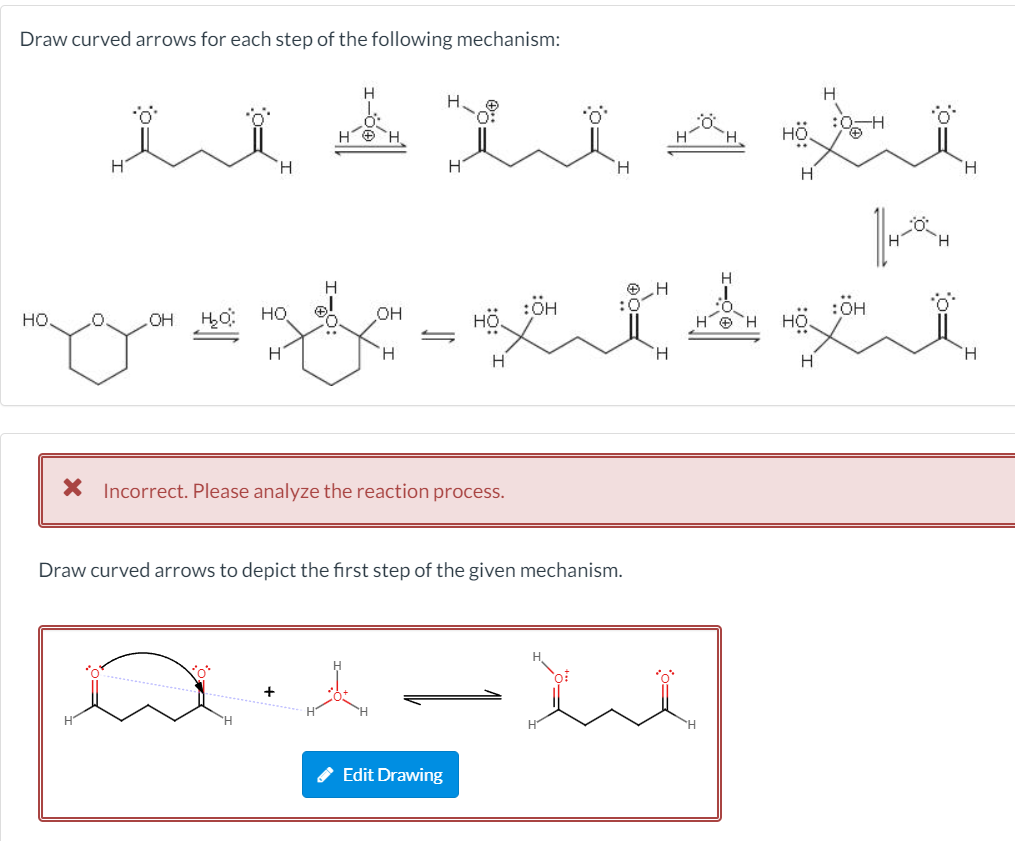
Draw Curved Arrows For The Following Reaction Step.
Draw Curved Arrows For The Following Reaction Step. - Web before you can do this you need to understand that a bond is due to a pair of electrons shared between atoms. This problem has been solved! Include formal charges and curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in all steps. Web the following reaction proceeds via an sn1 mechanism. *.82 submit answer retry entire group 8 more group attempts remaining noting the curved arrows, draw all the product (s), organic and inorganic, of the following reaction hh0h h. Draw step 3 of the mechanism. Drawing arrows heat h ott + h h h h :0: H с o p s ch & + oh f clos inen ci ch ch br practice problem 06.38 draw only curved arrows for each step of the following mechanism: Transition states occur at minima on reaction coordinate diagrams You may need to scroll to the right to see the link. When drawing hydrogen atoms on a carbon atom, either include all hydrogen atoms or none on that carbon atom, or your structure may be marked incorrect. Chapter 6 homework [reference question 1 1 pt draw curved arrows for the following reaction step. Web using curved arrows, draw the complete stepwise mechanism for the following reaction: Click the card to flip. This is because there is one bond formed (base grabbing the proton) and one bond broken (the acid releasing the proton). A doubled headed curved arrow means that one electron has been moved; Web add curved arrows to the following polar reaction to show the flow of electrons: The curved arrows represent the movement of electrons during a reaction, and. Then, pretend the reaction runs in reverse and add this many arrows to the products so that the reactant will be obtained ( backward problem) Web write a mechanism for the following reaction. Drawing arrows heat h ott + h h h h :0: Web the following reaction proceeds via an sn1 mechanism. Draw the curved arrows that accomplish the. Strategy look at the reaction, and identify the bonding changes that have occurred. You may need to scroll to the right to see the link. How many electron pairs change position in each reaction below? Step 1 is a loss of leaving group which i already figured out. Click the help link on the upper right for drawing instructions. Draw curved arrows for the following reaction step. Draw curved arrows to show where the electrons start from and where they end up in the following reactions: Strategy look at the reaction, and identify the bonding changes that have occurred. How many electron pairs change position in each reaction below? Web draw curved arrows to show electron reorganization for the. Draw step 3 of the mechanism. Include formal charges and curved arrows to show the movement of electrons in all steps. Ci n н nń oh ce + nen + 이 me me me. This problem has been solved! Web write a mechanism for the following reaction. Web curved arrows are used to show movement of protons; You may need to scroll to the right to see the link. Without knowing the specific reaction, it is impossible to draw the curved arrows for each step of the mechanism. Make certain that you can define, and use in context, the key terms below. Starting from the base and. Draw curved arrows to show where the electrons start from and where they end up in the following reactions: Web add curved arrows to the following polar reaction to show the flow of electrons: The convention below is for regiospecific electrophilic attack of a double bond. Include hydrogen atoms in your structure. Add this many arrows to the reactants so. This makes it easier to keep track of the bonds forming and breaking during the reaction as well as visualizing and explain more advanced features such as the region and stereochemistry of certain reactions. This problem has been solved! Web using curved arrows, draw the complete stepwise mechanism for the following reaction: You may need to scroll to the right. Draw step 3 of the mechanism. This is because there is one bond formed (base grabbing the proton) and one bond broken (the acid releasing the proton). A doubled headed curved arrow means that one electron has been moved; Step 2 is a nucleophilic attack which i have also done. Without knowing the specific reaction, it is impossible to draw. This is because there is one bond formed (base grabbing the proton) and one bond broken (the acid releasing the proton). You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Web add curved arrows to the following polar reaction to show the flow of electrons: Draw the mechanism for this reaction: Chapter 6 homework [reference question 1 1 pt draw curved arrows for the following reaction step. Web the following reaction proceeds via an sn1 mechanism. Strategy look at the reaction, and identify the bonding changes that have occurred. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Ci n н nń oh ce + nen + 이 me me me. Web draw curved arrows to show electron reorganization for the reaction step below. Which of the following correctly describes intermediates and/or transition states? Strategy look at the reaction, and identify the bonding changes that have occurred. Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Draw step 3 of the mechanism. Web using curved arrows, draw the complete stepwise mechanism for the following reaction: Web before you can do this you need to understand that a bond is due to a pair of electrons shared between atoms.Solved Q2 Draw curved arrows for each step of the
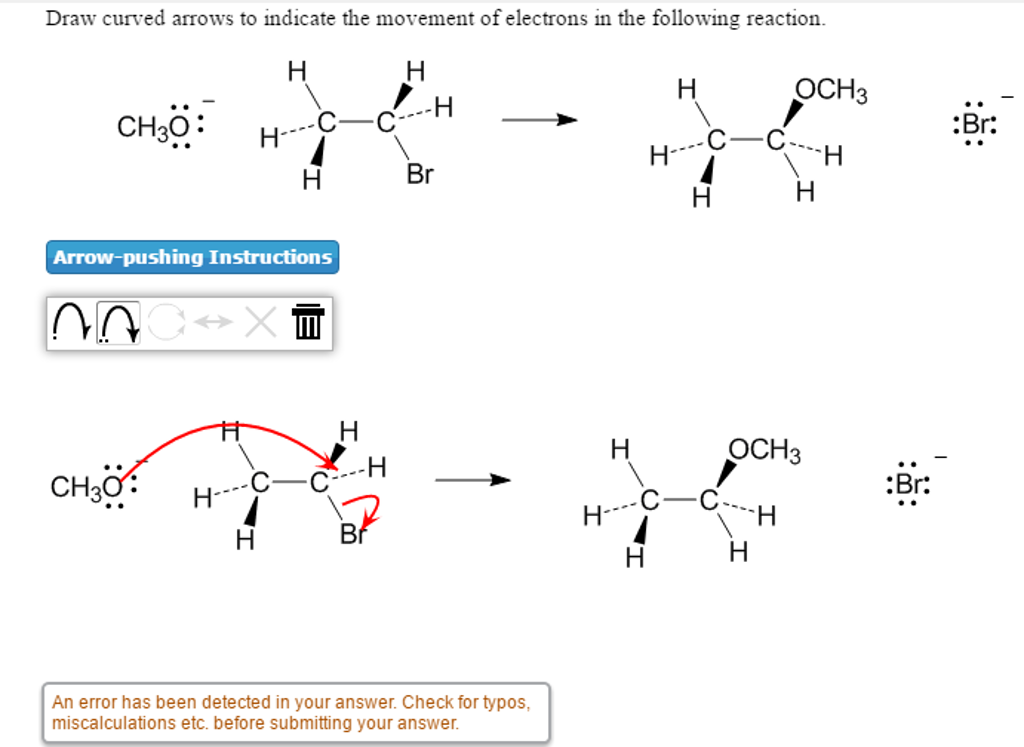
Solved Draw curved arrows to indicate the movement of
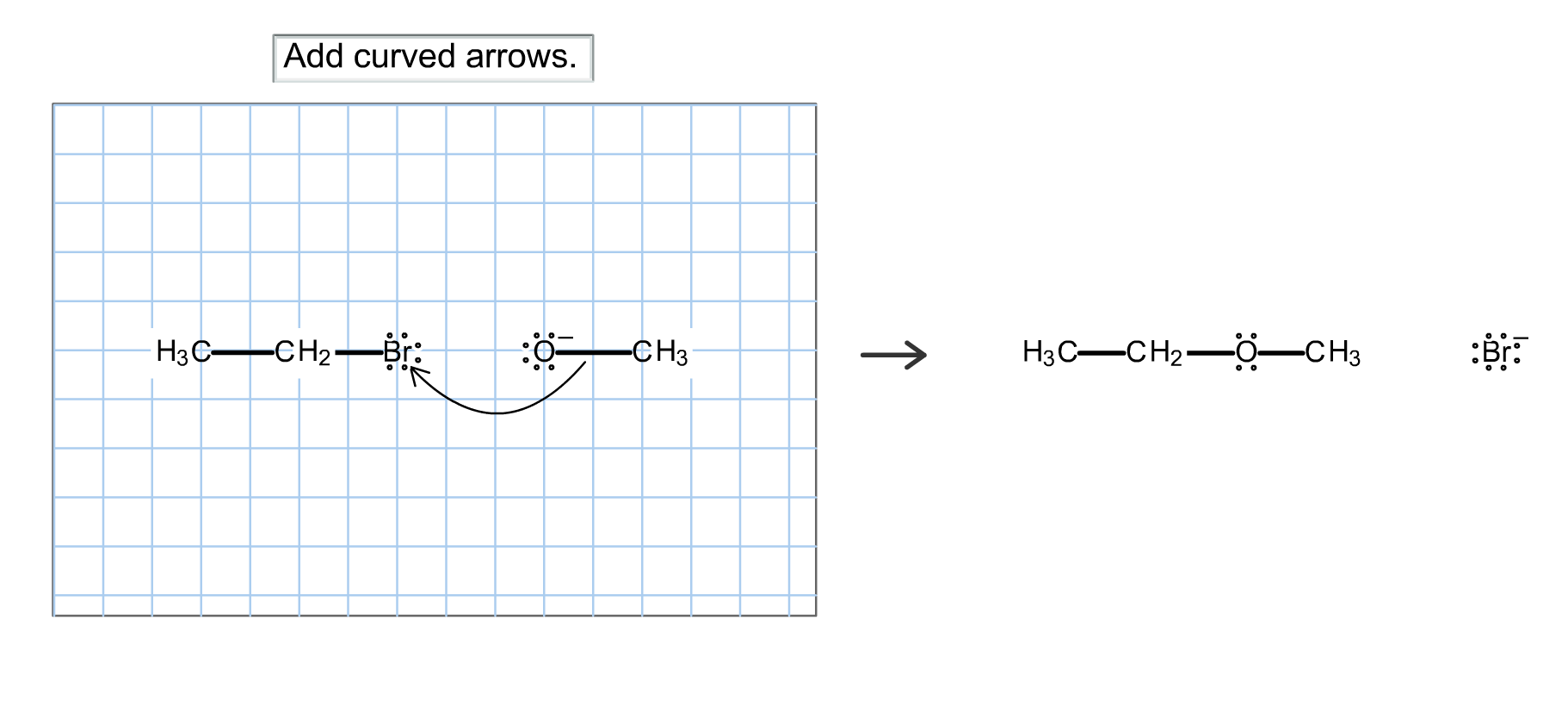
Given the following singlestep reaction, draw the curvedarrow
[Solved] Draw a curved arrow mechanism of the following reaction. Draw
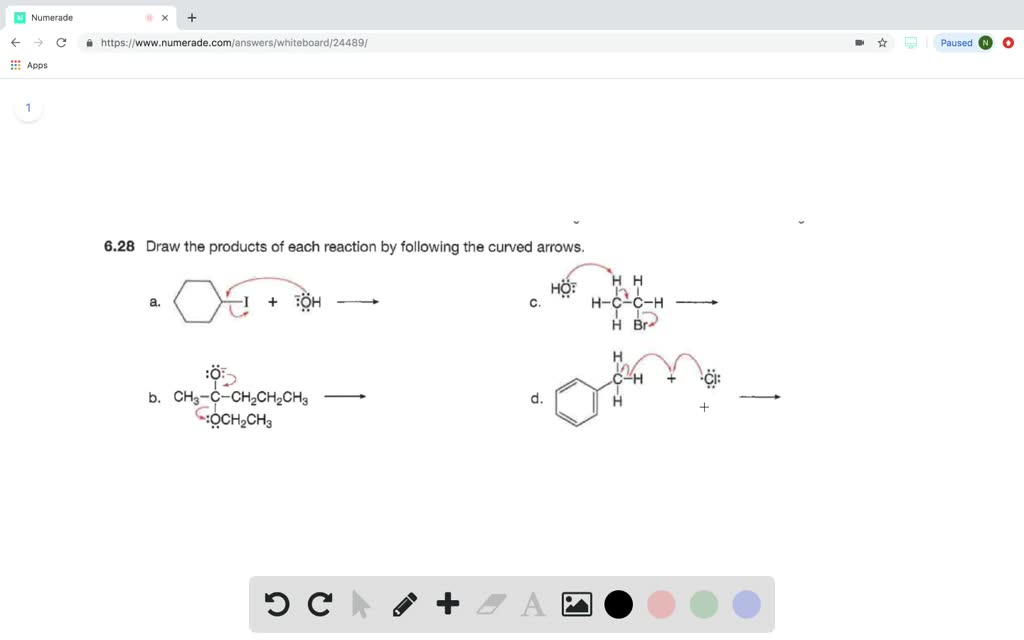
16. Using curved arrow notation, draw the reaction me… SolvedLib
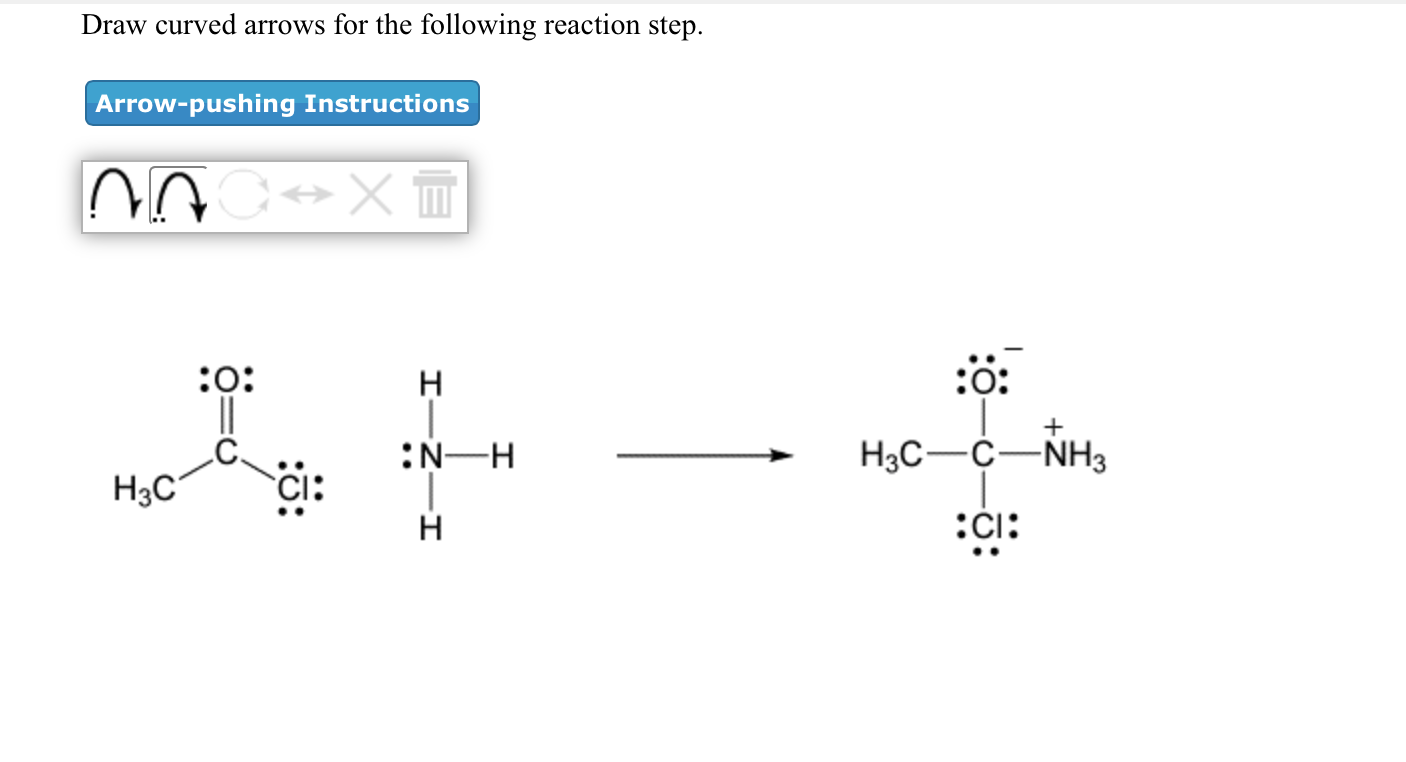
draw curved arrows for the following reaction step. jonnythemaynard
[Solved] Draw a curved arrow mechanism of the following reaction
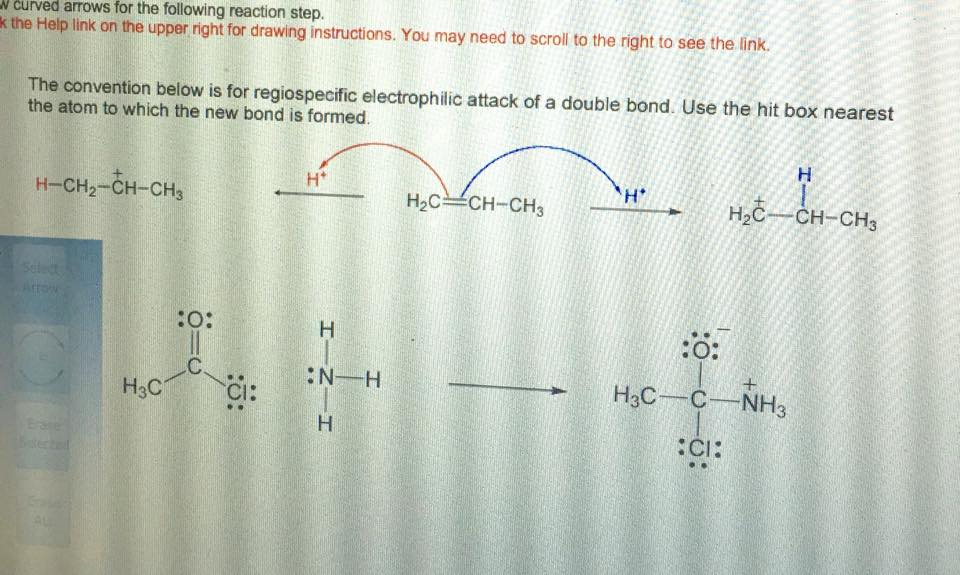
Solved Curved arrows for the following reaction step. the
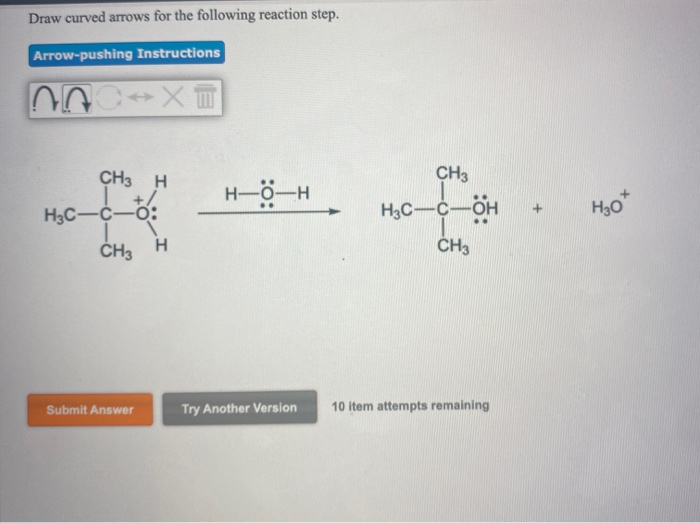
Solved Draw curved arrows for the following reaction step.
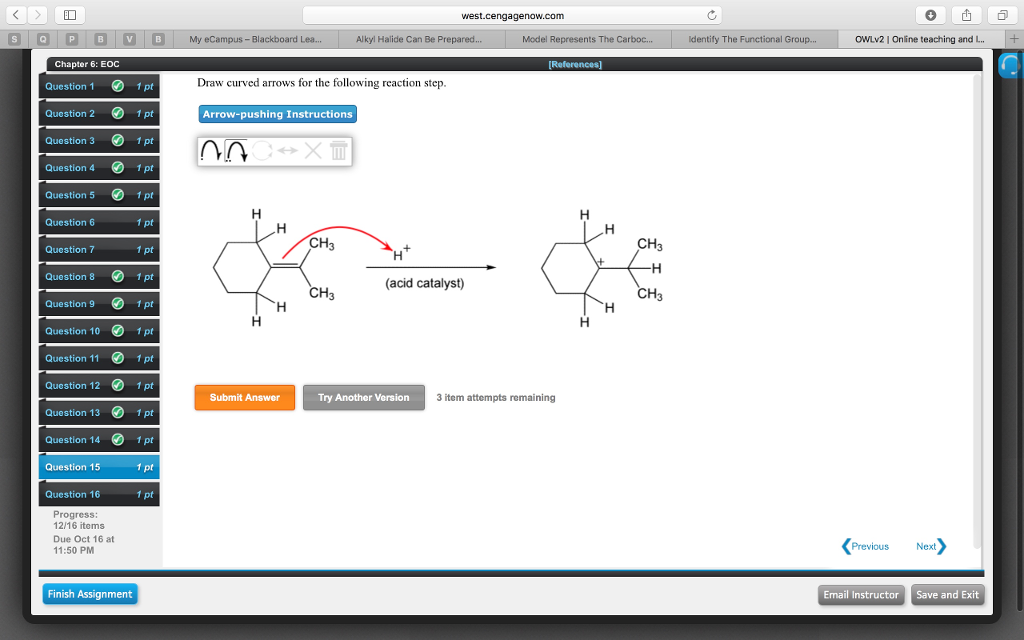
Solved Draw curved arrows for the following reaction step.
Web Write A Mechanism For The Following Reaction.
The Curved Arrows Represent The Movement Of Electrons During A Reaction, And The Specific Movement Of Electrons Depends On The Specific Reaction Being Studied.
You May Need To Scroll To The Right To See The Link.
Draw The Reaction Coordinate Diagram For The Sn1 Reaction In Problem 3 Above.
Related Post: