Draw The Lewis Structure For A Carbon Monosulfide Cs Molecule
Draw The Lewis Structure For A Carbon Monosulfide Cs Molecule - Lewis structures are representations of molecules that include not only what atoms are present in the molecule but also how the atoms are connected. The following procedure can be used to draw lewis structure for simple molecules. Counting total valence electrons of atoms. Web draw the lewis dot diagram for carbon. Web the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule is attached in the attachment below. Web get the detailed answer: The following procedure will give you the correct lewis structure for any molecule or polyatomic ion that has one central atom. Web the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule and ar are attached. It is an organo sulphur compound. Draw lewis structures for covalent compounds. Draw lewis structures for covalent compounds. ° = a + b*t + c*t h° − h° = a*t + b*t /2 + c*t /3 + d*t /4 − e/t + f − h s° = a*ln (t) + b*t + c*t /2 + d*t /3 − e/ (2*t c = heat capacity (j/mol*k) h° = standard enthalpy (kj/mol) s° =. Web carbon monosulfide is a chemical compound with the formula cs. Web verified answer carbon monosulfide lewis structure The following procedure will give you the correct lewis structure for any molecule or polyatomic ion that has one central atom. In doing so, that bond uses up two valence electrons. This diatomic molecule is the sulfur analogue of carbon monoxide, and. Draw the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule. Lewis structures are also called as electron dot structures and can be drawn if the molecular formula of a compound is known. In doing so, that bond uses up two valence electrons. Both the oxygen and the carbon now have an octet of electrons, so this is an acceptable lewis. Web the following procedure can be used to construct lewis electron structures for simple molecules. The following procedure can be used to draw lewis structure for simple molecules. Web the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule and ar are attached. Draw and explain the lewis dot structure of carbon. Therefore, the carbon and sulfur in this. Data last reviewed in december, 1976. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Therefore, the carbon and sulfur in this. In all cases, these bonds involve the sharing or transfer of valence shell electrons between atoms. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core. Web draw the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule 谲 alo ar this problem has been solved! In doing so, that bond uses up two valence electrons. Web the carbon monosulfide lewis structure consists of a carbon atom bonded to a sulfur atom. Draw the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide molecule. Web drawing lewis structures for molecules. [1] the molecule resembles carbon monoxide with a triple bond between carbon and sulfur. Draw the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule. Web writing lewis structures for diatomic molecules draw the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule. Counting total valence electrons of atoms. Web to draw the lewis structure for carbon monosulfide, we first need to. Counting total valence electrons of atoms. Web the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule and ar are attached. Before we can begin drawing the lewis structure for cos (carbon monosulfide), we need to determine the total number of valence electrons present in the molecule.valence electrons are the outermost electrons of an atom that participate in chemical bonding. Web. Web the following procedure can be used to construct lewis electron structures for simple molecules. An atom of carbon has a total of 4 valence electrons, while an atom of sulfur has a total of 6 valence electrons. The oxygen also has two lone pairs drawn. Web carbon monosulfide is a chemical compound with the formula cs. This diatomic molecule. This diatomic molecule is the sulfur analogue of carbon monoxide, and is unstable as a solid or a liquid, but it has been observed as a gas both in the laboratory and in the interstellar medium. Then what we do is we bond the carbon to the sulfur. Co x 5 this problem has been solved! Web writing lewis structures. Therefore, there are a total of ten valence electrons present in the cs molecule (six plus four equals ten). Co x 5 this problem has been solved! To count the valence electrons in cos,. Web draw the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule 谲 alo ar this problem has been solved! Web verified answer carbon monosulfide lewis structure Lewis structures are also called as electron dot structures and can be drawn if the molecular formula of a compound is known. Lewis structures are representations of molecules that include not only what atoms are present in the molecule but also how the atoms are connected. Web the bond between the oxygen and carbon is replaced with a double bond. Draw the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide molecule. You'll get a detailed solution from a subject matter expert that helps you learn core concepts. Data last reviewed in december, 1976. Web get the detailed answer: Web the carbon monosulfide lewis structure consists of a carbon atom bonded to a sulfur atom. Web the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule and ar are attached. Web carbon monosulfide is a chemical compound with the formula cs. Draw lewis structures for covalent compounds.
FileCarbon Lewis Structure PNG.png Wikimedia Commons
[Solved] Choose the Lewis dot formula that most accurately describes

CS2 Lewis Structure, Hybridization, Polarity and Molecular Shape
Carbon Monosulfide Lewis Dot Structure bmptootles

Lewis Diagram Of Carbon

Lewis Structure Types

How to Draw Lewis Structures

Carbon Monosulfide Lewis Dot Structure bmptootles
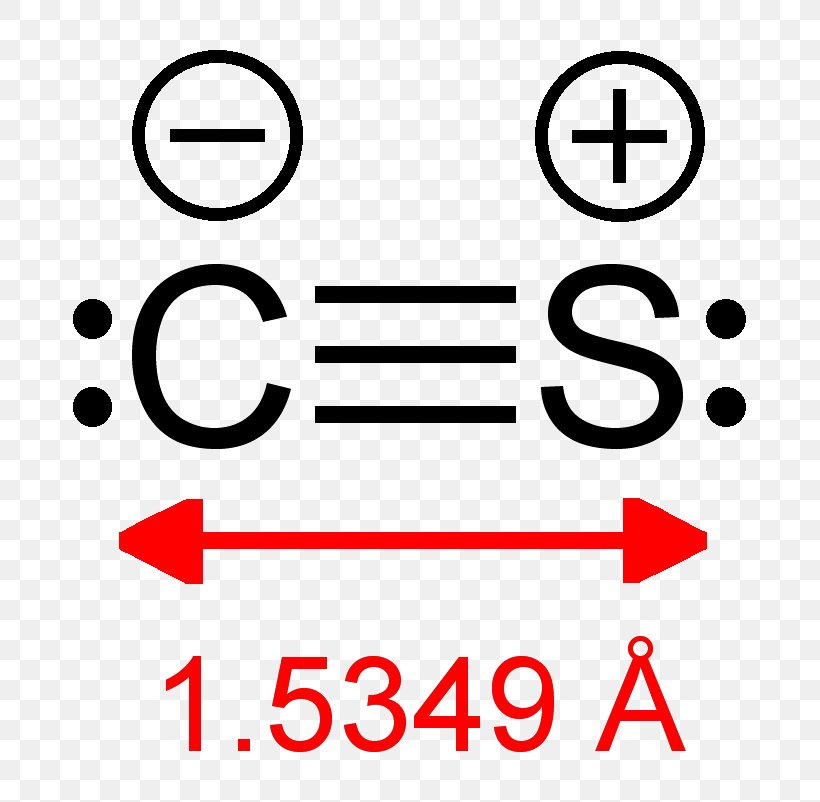
Carbon Monosulfide Lewis Structure Molecule Carbon Monoxide, PNG

Carbon Monosulfide Molecule Stock Vector Illustration of sphere
° = A + B*T + C*T H° − H° = A*T + B*T /2 + C*T /3 + D*T /4 − E/T + F − H S° = A*Ln (T) + B*T + C*T /2 + D*T /3 − E/ (2*T C = Heat Capacity (J/Mol*K) H° = Standard Enthalpy (Kj/Mol) S° = Standard Entropy (J/Mol*K) T.
You'll Get A Detailed Solution From A Subject Matter Expert That Helps You Learn Core Concepts.
The Oxygen Also Has Two Lone Pairs Drawn.
Web Draw The Lewis Dot Diagram For Carbon.
Related Post: