Drawing Of An Enzyme
Drawing Of An Enzyme - Web tanja ivanova/getty images the majority of enzymes are proteins, though some are ribonucleic acid (rna) molecules. Web to describe how ph, temperature, and the concentration of an enzyme and its substrate influence enzyme activity. For example, proteases (enzymes that break peptide bonds in proteins) will not work on starch (which is broken down by the enzyme amylase). Web the functionality of an enzyme is determined by the shape of the enzyme. The human genome encodes for over 20,000 different proteins, thousands of which are enzymes. Web to describe how ph, temperature, and the concentration of an enzyme and its substrate influence enzyme activity. Web enzymes made of amino acids that are arranged in a polypeptide chain produce the primary structure. Web as you view enzyme animation, focus on this concept: Web a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction—without being a reactant—is called a catalyst. Web enzymes are highly specific catalysts for biochemical reactions, with each enzyme showing a selectivity for a single reactant, or substrate. The single most important property of enzymes is the ability to increase the rates of reactions occurring in living organisms, a property known as catalytic activity. “by conforming to a similar structure as standard base pairs, our synthetic base pairs can slip in under the radar and be incorporated in the. The active site of an enzyme recognizes, confines, and. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein enzymes. They are the “gnomes” inside each one of us that take molecules like nucleotides and align them together to create dna, or amino acids to make proteins, to name two of thousands of such functions. Energy is also released during the reaction. They provide a lot of. Enzymes are usually proteins, though some ribonucleic acid (rna) molecules act as enzymes too. Rna molecules translate information from dna and create proteins. It regulates cell chemistry so that the proper reactions occur in the proper place at the proper time. The products of the reaction are carbon dioxide (co 2) and water (h 2 o). Web tanja ivanova/getty images. The reaction represented by this graph is a combustion reaction involving the reactants glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) and oxygen (o 2 ). The enzyme recognizes the shape of its substrate and it is able to hold it in position in what is called the active site. The single most important property of enzymes is the ability to. Enzymes are usually proteins, though some ribonucleic acid (rna) molecules act as enzymes too. Web to describe how ph, temperature, and the concentration of an enzyme and its substrate influence enzyme activity. Almost every chemical reaction in the biological world is catalyzed by protein enzymes. It regulates cell chemistry so that the proper reactions occur in the proper place at. Web schematic drawing of an enzyme reaction www.sciencebuddies.org. Enzymes are usually proteins, though some ribonucleic acid (rna) molecules act as enzymes too. The reactants of enzyme catalyzed reactions are called substrates. The area in which bonds of the reactant(s) are broken is known as the active site. “in biology, structure determines function,” said wang. Web enzymes are potent catalysts. Web an enzymes is a protein that facilitates a cellular metabolic process by lowering activation energy (ea) levels in order to catalyze the chemical reactions between biomolecules. Enzymes are proteins that act upon substrate molecules and decrease the activation energy necessary for a chemical reaction to occur by stabilizing the transition state. The total number. The enzymes that transcribe dna can’t tell the difference between these synthetic base pairs and those found in nature. Web as you view enzyme animation, focus on this concept: The biological processes that occur within all living organisms are chemical reactions, and most are. Web introduction to enzymes mechanisms. Web an enzymes is a protein that facilitates a cellular metabolic. The reactants of enzyme catalyzed reactions are called substrates. Web tanja ivanova/getty images the majority of enzymes are proteins, though some are ribonucleic acid (rna) molecules. The enormous catalytic activity of enzymes can perhaps best be expressed by a constant, k cat, that is variously referred to as the turnover rate, turnover frequency or turnover number.this constant represents the number. The reaction represented by this graph is a combustion reaction involving the reactants glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) and oxygen (o 2 ). For example, proteases (enzymes that break peptide bonds in proteins) will not work on starch (which is broken down by the enzyme amylase). Web basic enzyme kinetics graphs graphs like the one shown below (graphing. “by conforming to a similar structure as standard base pairs, our synthetic base pairs can slip in under the radar and be incorporated in the. The products of the reaction are carbon dioxide (co 2) and water (h 2 o). The human genome encodes for over 20,000 different proteins, thousands of which are enzymes. The single most important property of enzymes is the ability to increase the rates of reactions occurring in living organisms, a property known as catalytic activity. Web schematic drawing of an enzyme reaction www.sciencebuddies.org. The enzymes break down fatty acids and amino acids, and they also detoxify some substances that enter the body. Öoeo science buddies substrate active site enzyme enzyme/substrate complex enzyme proaucts enzyme. The enormous catalytic activity of enzymes can perhaps best be expressed by a constant, k cat, that is variously referred to as the turnover rate, turnover frequency or turnover number.this constant represents the number of substrate molecules that can be converted to product by a single enzyme molecule. Web enzyme, a substance that acts as a catalyst in living organisms, regulating the rate at which chemical reactions proceed without itself being altered in the process. Web enzymes made of amino acids that are arranged in a polypeptide chain produce the primary structure. Web as you view enzyme animation, focus on this concept: This suffix indicates that a molecule is an enzyme. Metabolic processes and other chemical reactions in the cell are carried out by a set of enzymes that are necessary to sustain life. Web “enzymes can be defined as biological polymers that catalyze biochemical reactions.” the majority of enzymes are proteins with catalytic capabilities crucial to perform different processes. Web enzymes are the catalysts involved in biological chemical reactions. For example, the enzyme acetylcholinesterase catalyzes the decomposition of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine to choline and acetic acid.
Enzymes Definition, Classification & Functions

Enzyme & Their Substrates Mode of Action Plantlet

Enzyme structure (HIGHER) YouTube

Enzymes Definition, Classification & Functions

Enzyme substrates and active sites chemical Vector Image
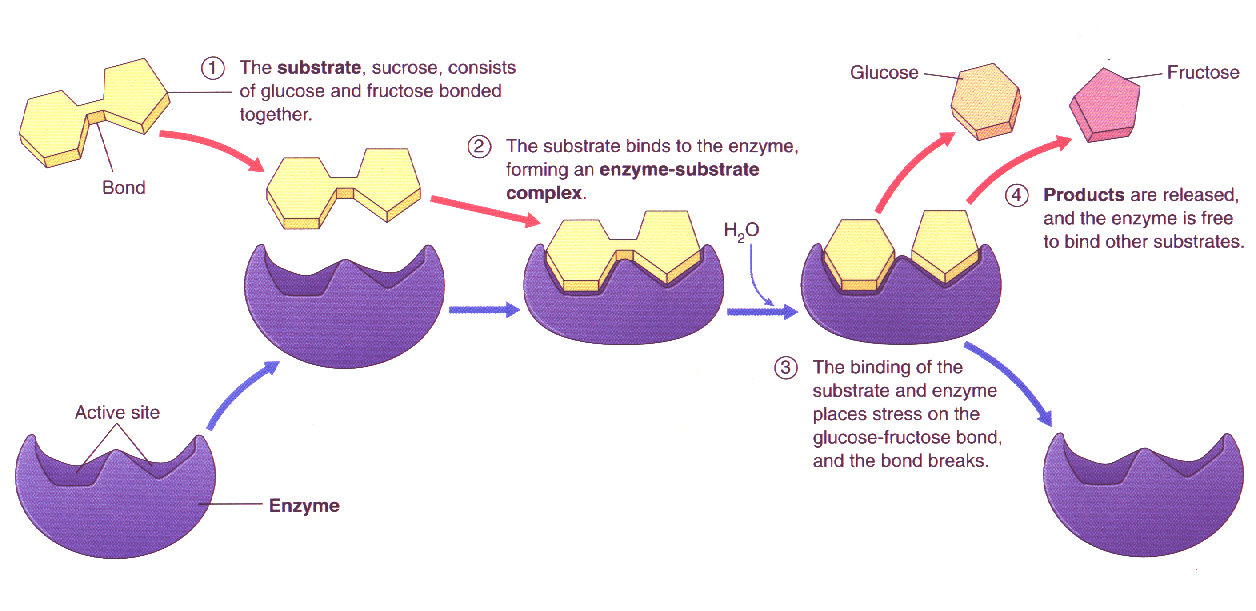
Chapter 8 Enzymes
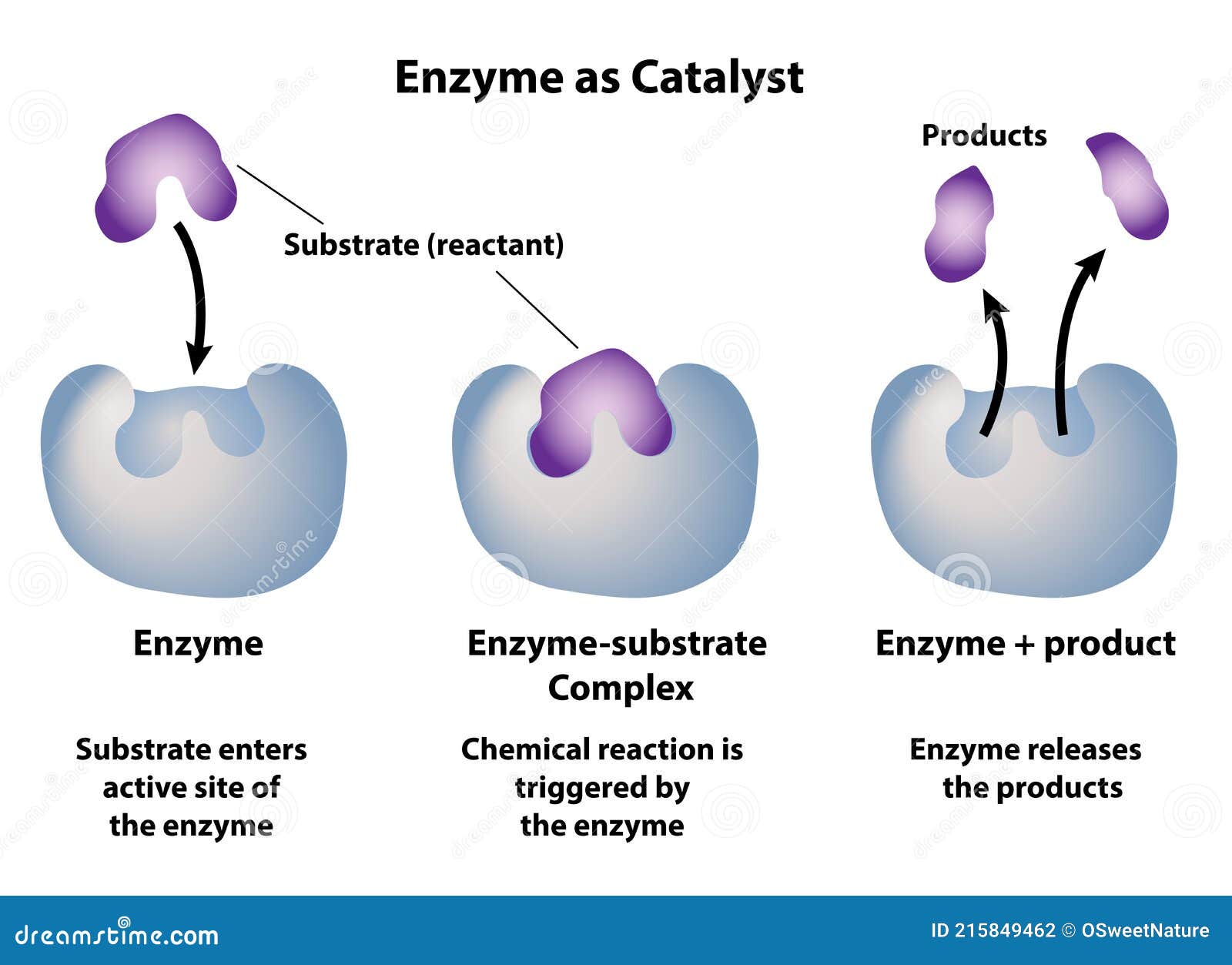
Enzyme As Catalyst in Chemical Reactions Stock Vector Illustration of
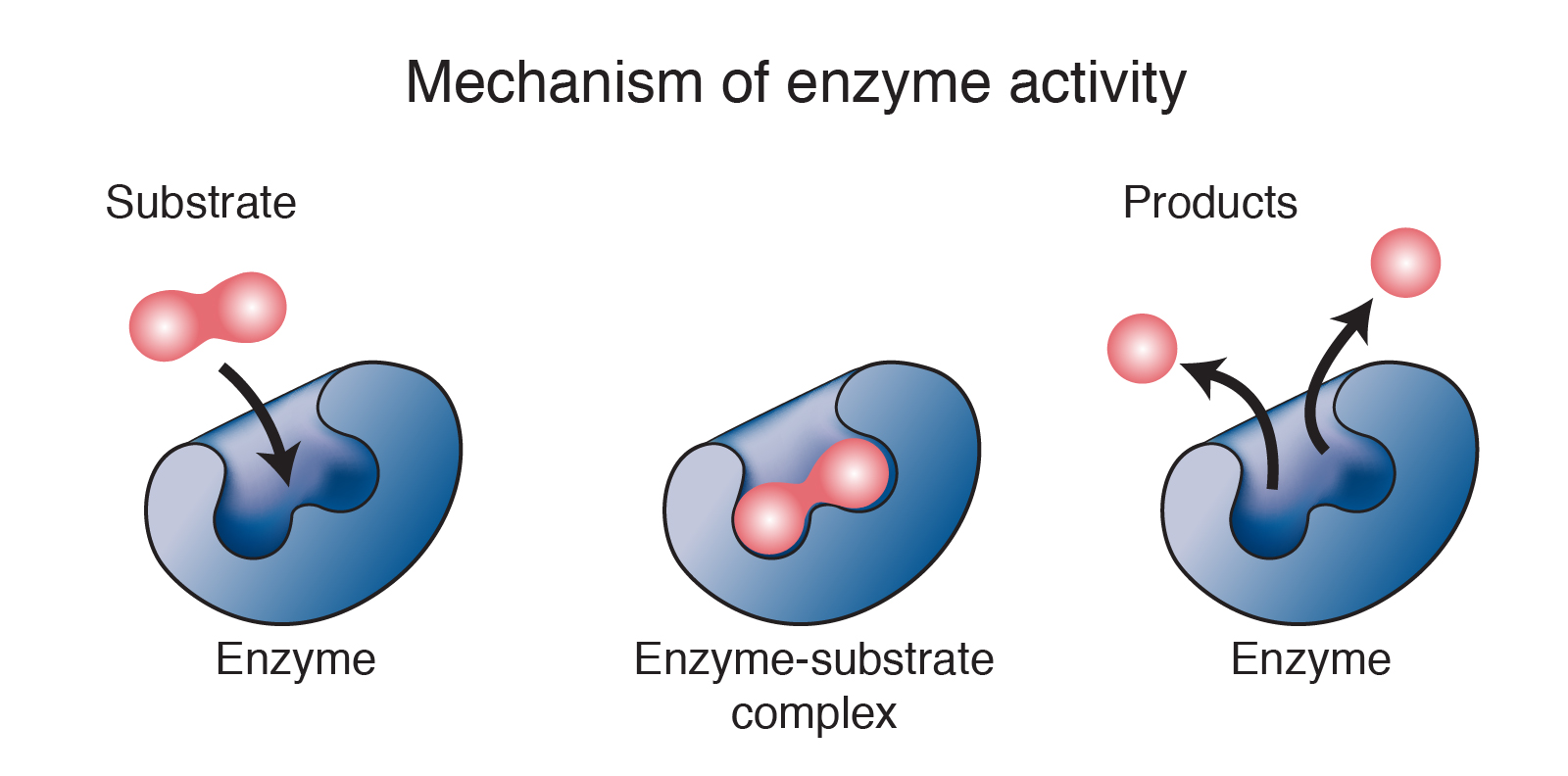
Enzyme

Enzyme vector illustration. Full labeled cycle and diagram with
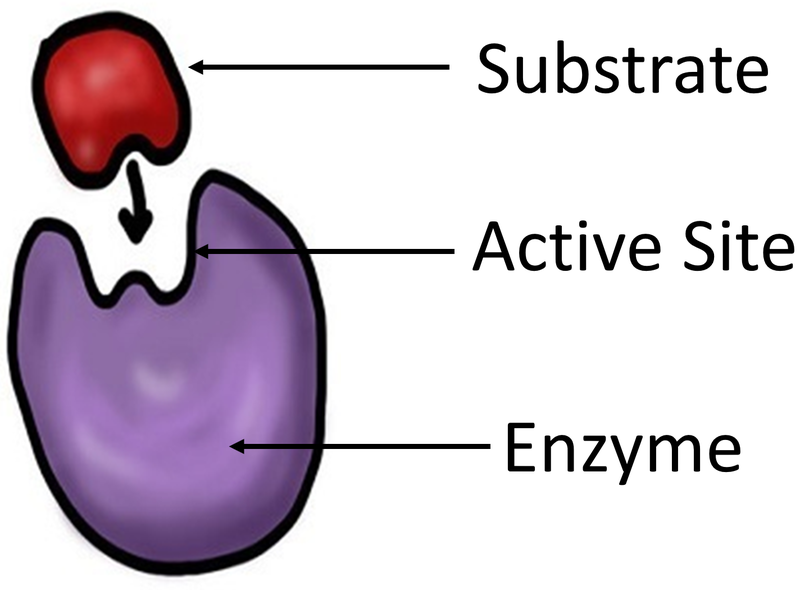
Enzyme Key Stage Wiki
Web Peptide Bond Formation Mechanism.
For Example, Proteases (Enzymes That Break Peptide Bonds In Proteins) Will Not Work On Starch (Which Is Broken Down By The Enzyme Amylase).
Enzymes Are Proteins That Act Upon Substrate Molecules And Decrease The Activation Energy Necessary For A Chemical Reaction To Occur By Stabilizing The Transition State.
Web Browse 430+ Enzyme Drawing Stock Photos And Images Available, Or Start A New Search To Explore More Stock Photos And Images.
Related Post: