Drawing Of Lipids
Drawing Of Lipids - Web lipids, as a class of compounds, are insoluble in water but are soluble in other organic solvents. Soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, chloroform, acetone, benzene, etc. Pure fats and oils are colorless, odorless, and tasteless. Describe phospholipids and their role in cells; Web we can draw a cartoon model of this as a circle representing the polar end or head group with two connecting lines representing the two long nonpolar tails. Lipid, any of a diverse group of organic compounds including fats, oils, hormones, and certain components of membranes that are grouped together because they do not interact appreciably with water. Web lipids are not defined by the presence of specific functional groups, as carbohydrates are, but by a physical property—solubility. Explain the role of fats in storing energy; A hydrogen you found in a water molecule (h20) is the same as a hydrogen in a methyl molecule (ch3). They provide cell membrane structure and resilience, insulation, energy storage, hormones and protective barriers. Web lipids are biological molecules that are insoluble in water. There are three main types of lipids: Web lipids form a major component of all types of biological membranes. Lipids serve many important biological roles. Vector diagram vector set of brown, beige and white fat cells. There are three main types of lipids: It consists mainly of a lipoprotein bilayer. Web describe the four major types of lipids; Fat in food serves as an energy source with high caloric density, adds texture and taste, and contributes to. Biological lipids usually refer to a broad grouping of naturally occurring molecules which includes fatty acids, waxes, eicosanoids, monoglycerides,. So let's probe their structures. Web lipids make up a group of compounds including fats, oils, steroids and waxes found in living organisms. They provide cell membrane structure and resilience, insulation, energy storage, hormones and protective barriers. Web a lipid is generally considered to be any molecule that is insoluble in water and soluble in organic solvents. Fats have glycerol. Web lipids form a major component of all types of biological membranes. Soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, chloroform, acetone, benzene, etc. Web properties of lipids. On this page, we’ll learn about the structures of these three types of lipids, as well as their functions in the body and where you can find them. Web lipids, as a class of. The three main types of lipids are phospholipids, sterols (including the different types of. Learn more about the structure, types, and functions of lipids in this article. Vector diagram vector set of brown, beige and white fat cells. They provide cell membrane structure and resilience, insulation, energy storage, hormones and protective barriers. Web lipids are biological molecules that are insoluble. Web 8 years ago this is a great question; Lipids serve many important biological roles. Describe phospholipids and their role in cells; On this page, we’ll learn about the structures of these three types of lipids, as well as their functions in the body and where you can find them. Fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, cardiolipins, sphingolipids, sterols, and sphingolipid glycans. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids; The cytoplasmic membrane which is the limiting layer separating the biological cell from the outer environment is present universally in all organisms. As we saw with proteins, lipid structure mediates their function. Explain the role of fats in storing energy; You probably know that all elements of the same type are essentially the. The three main types of lipids are phospholipids, sterols (including the different types of. There are three main types of lipids: They also play a role in diseases. Lipids serve many important biological roles. You probably know that all elements of the same type are essentially the same; There are three main types of lipids: These molecules yield high energy and are responsible for different functions within the human body. Web lipids are biological molecules that are insoluble in water. Soluble in organic solvents like alcohol, chloroform, acetone, benzene, etc. Web the lipid maps website currently contains a suite of structure drawing tools for the following lipid categories: Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids; The cytoplasmic membrane which is the limiting layer separating the biological cell from the outer environment is present universally in all organisms. Biological lipids usually refer to a broad grouping of naturally occurring molecules which includes fatty acids, waxes, eicosanoids, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, sphingolipids, sterols, terpenes, prenols. Biomolecules properties of lipids lipids. Lipids help regulate hormones, transmit nerve impulses, cushion organs, and store energy in the form of body fat. As we saw with proteins, lipid structure mediates their function. Compounds isolated from body tissues are classified as lipids if they are more soluble in organic solvents, such as dichloromethane, than in water. Web lipids make up a group of compounds including fats, oils, steroids and waxes found in living organisms. Differentiate between saturated and unsaturated fatty acids; Biological lipids usually refer to a broad grouping of naturally occurring molecules which includes fatty acids, waxes, eicosanoids, monoglycerides, diglycerides, triglycerides, phospholipids, sphingolipids, sterols, terpenes, prenols. The cytoplasmic membrane which is the limiting layer separating the biological cell from the outer environment is present universally in all organisms. Most popular fat cells fat cells from white adipose tissue. There are three main types of lipids: Define the basic structure of a steroid and some steroid functions; On this page, we’ll learn about the structures of these three types of lipids, as well as their functions in the body and where you can find them. Triglycerides (fats), waxes, steroids, and phospholipids. It consists mainly of a lipoprotein bilayer. Examples of such solvents include acetone and ether. Web lipids are not defined by the presence of specific functional groups, as carbohydrates are, but by a physical property—solubility. Fatty acyls, glycerolipids, glycerophospholipids, cardiolipins, sphingolipids, sterols, and sphingolipid glycans.2.8 Lipids Biology LibreTexts

Lipids Microbiology

Lipids Boundless Biology
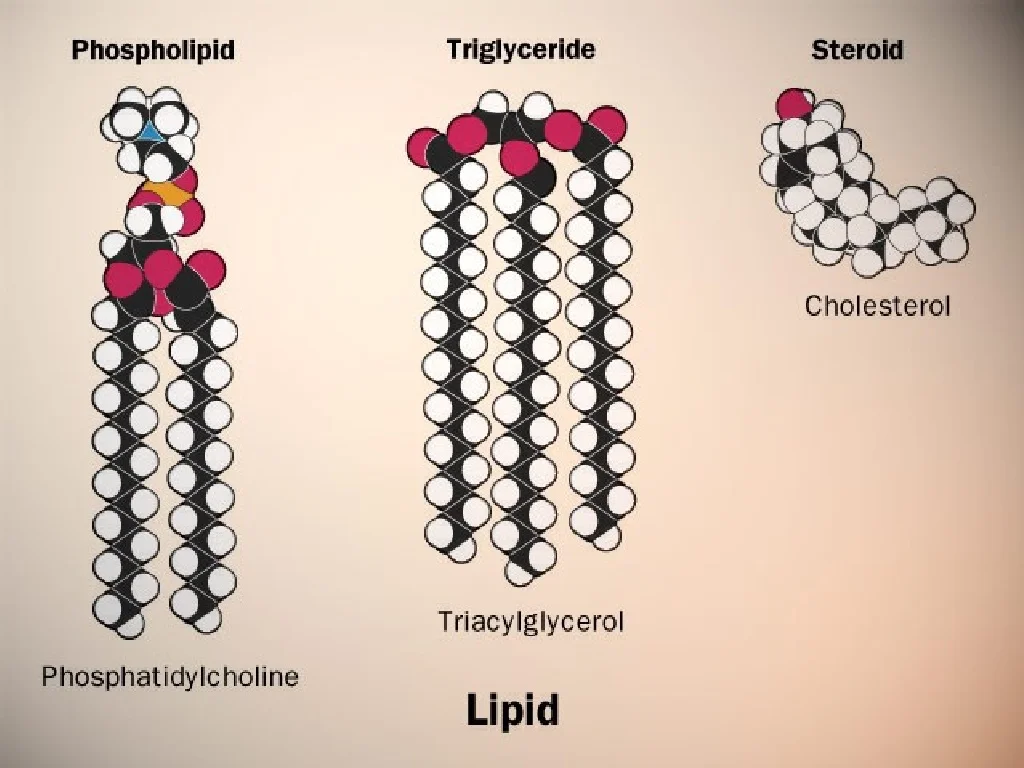
Lipids
A schematic drawing of coarsegrained model of lipid molecule. The
Lipids Chemistry Structure & Function
PPT Lipids PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID6999007

Lipids Biology for NonMajors I

Lipids Biology for NonMajors I
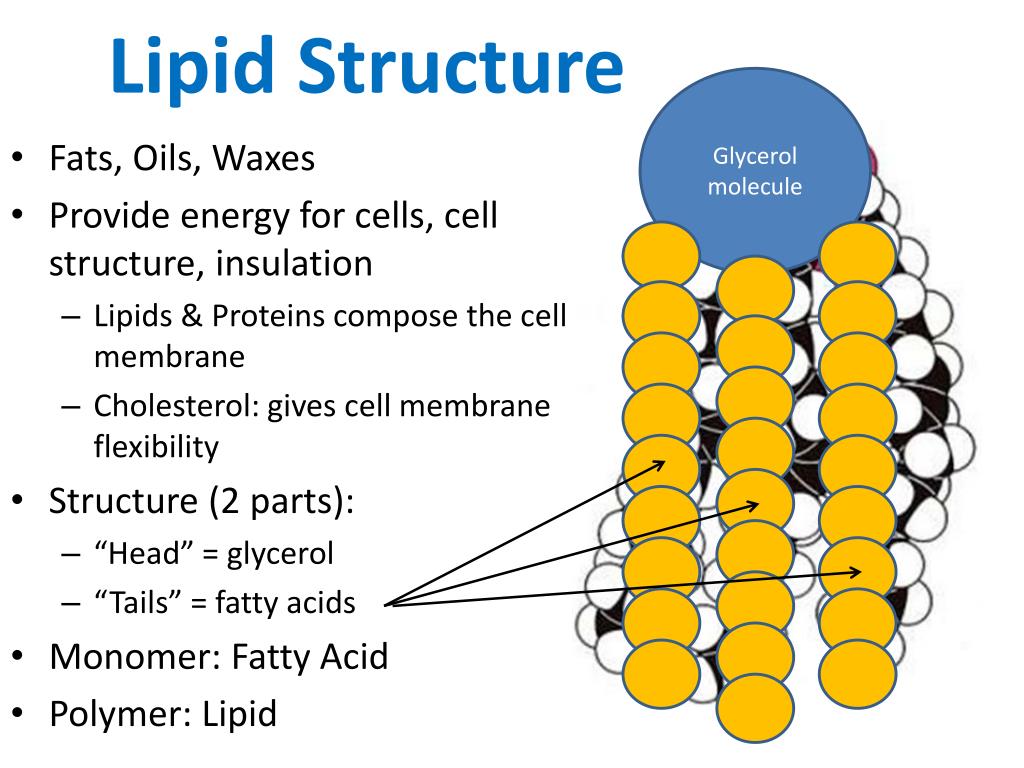
Lipids
Web Lipids, As A Class Of Compounds, Are Insoluble In Water But Are Soluble In Other Organic Solvents.
Biomolecules Properties Of Lipids Lipids Are A Family Of Organic Compounds, Composed Of Fats And Oils.
There Are Three Main Types Of Lipids:
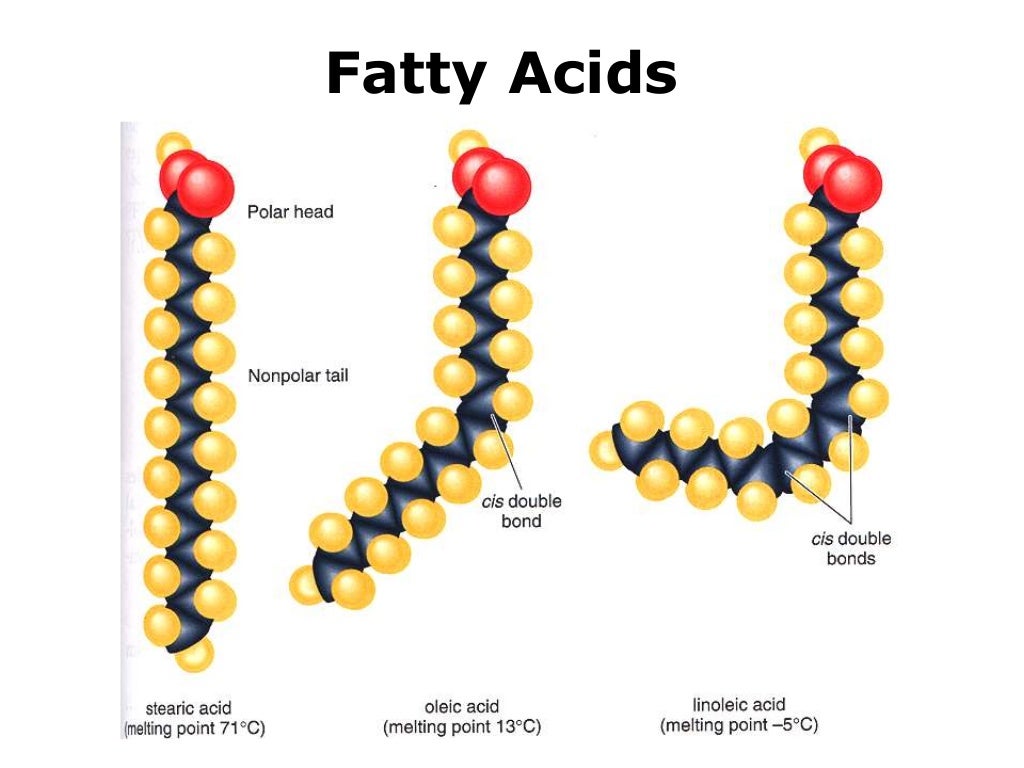
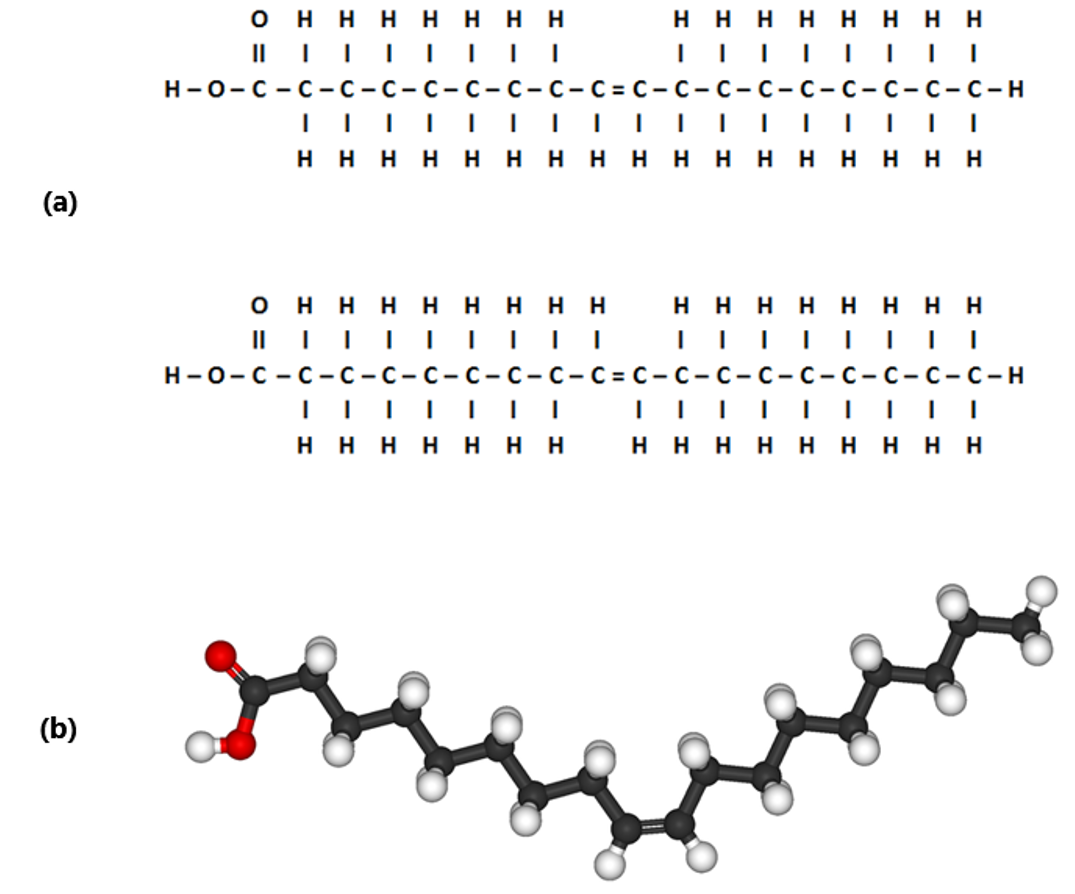
Web How To Draw Saturated And Unsaturated Fatty Acids Plus Some Ad Information About Unsaturated Fatty Acids
Related Post: