Drawing Of The Carbon Cycle
Drawing Of The Carbon Cycle - Yellow numbers are natural fluxes, and red are human contributions in gigatons of carbon per year. Carbon moves from plants to animals. Through the process of photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is pulled from the air to produce food made from carbon for plant growth. Carbon dioxide is present in the atmosphere as a gas. Carbon compounds regulate the earth’s temperature, make up the food that sustains us, and provide energy that fuels our global economy. Web carbon cycle diagram education in chemistry april 2021 rsc.li/2p939rc. There are arrows pointing from air sea gas exchange, human emissions, and a volcano pointing towards carbon dioxide in atmosphere. White numbers indicate stored carbon. From how to teach the carbon cycle at 11 14, education in chemistry, rsc.li/2p939rc keywords carbon cycle, earth science, atmosphere. The entire carbon cycle is shown in figure 1. Exchange of carbon dioxide between the ocean and the atmosphere takes place at the surface. Climate literacy carbon capture and storage education carbon is the chemical backbone of life on earth. Web carbon moves from the atmosphere to plants. Carbon dioxide is present in the atmosphere as a gas. Animals eat plants, metabolize the molecules, and release carbon dioxide. Locate the carbon cycle icon and identify other earth system processes and phenomena that cause changes to, or are affected by, the cycling of carbon. ( diagram adapted from u.s. Animals eat plants, metabolize the molecules, and release carbon dioxide. Web the carbon cycle describes the continuous flow of carbon between organic and inorganic carbon reservoirs, or areas of earth. Carbon dioxide gas exists in the atmosphere and is. The overall effect is that carbon is constantly recycled in the dynamic processes taking place in the atmosphere, at the surface and in the crust of the earth. Researchers say the artworks could be up to 19,000 years old. Carbon is a constituent of all organic compounds, many of which are. Doe, biological and environmental research information. Most of earth’s carbon is found in inorganic reservoirs such as rocks, water, and sediments. Web the ocean plays an important part in the carbon cycle. Like car windows on a sunny day, carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases help trap the sun’s heat, keeping it close to earth’s surface. Web a drawing of. Carbon dioxide gas exists in the atmosphere and is. Researchers say the artworks could be up to 19,000 years old. Human activities involving fossil fuels, including manufacturing, transportation, and agriculture, release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere in large. Carbon is the fourth most abundant element in the universe. Web a drawing of mountains, rocks and the ocean titled the carbon. Web where does all the carbon go? Some of the carbon dioxide stays as dissolved gas, but much of it gets turned into other. Carbon compounds regulate the earth’s temperature, make up the food that sustains us, and provide energy that fuels our global economy. Cut out these cards and use them to make your own diagram of the carbon. Climate literacy carbon capture and storage education carbon is the chemical backbone of life on earth. This cycle keeps carbon circulating in the biosphere. The vast majority of carbon resides as inorganic minerals in. Yellow numbers are natural fluxes, and red are human contributions in gigatons of carbon per year. With its ability to form complex molecules such as dna. Exchange of carbon dioxide between the ocean and the atmosphere takes place at the surface. Like car windows on a sunny day, carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases help trap the sun’s heat, keeping it close to earth’s surface. Web carbon cycle, in biology, circulation of carbon in various forms through nature. Carbon is the fourth most abundant element in. Carbon dioxide is present in the atmosphere as a gas. Carbon is a constituent of all organic compounds, many of which are essential to life on earth. Climate literacy carbon capture and storage education carbon is the chemical backbone of life on earth. Web carbon cycle represents the movement of carbon in elemental and combined states on earth. Locate the. Carbon in the form of carbon dioxide. To an extent, this is a good thing. Web this fairly basic carbon cycle diagram shows how carbon atoms 'flow' between various 'reservoirs' in the earth system. These are the reservoirs, or sinks, through which. This cycle keeps carbon circulating in the biosphere. Some of the carbon dioxide stays as dissolved gas, but much of it gets turned into other. Yellow numbers are natural fluxes, and red are human contributions in gigatons of carbon per year. Without that warming, earth would be a ball of ice. Like car windows on a sunny day, carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases help trap the sun’s heat, keeping it close to earth’s surface. Exchange of carbon dioxide between the ocean and the atmosphere takes place at the surface. These are the reservoirs, or sinks, through which. Microorganisms are vital for these cycles. Web carbon cycle diagram education in chemistry april 2021 rsc.li/2p939rc. Carbon is the fourth most abundant element in the universe. Overall, the ocean is called a carbon ‘sink’ because it takes up more carbon from the atmosphere than it gives up. Web carbon cycle shows the movement of carbon in elemental and combined states on earth. Carbon in the form of carbon dioxide. Web global change infographic the carbon cycle is an essential part of how the earth system works. Animals eat plants, metabolize the molecules, and release carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide is present in the atmosphere as a gas. Web the entire carbon cycle is shown in figure 5.3.
Carbon Cycle Diagram from NASA Center for Science Education
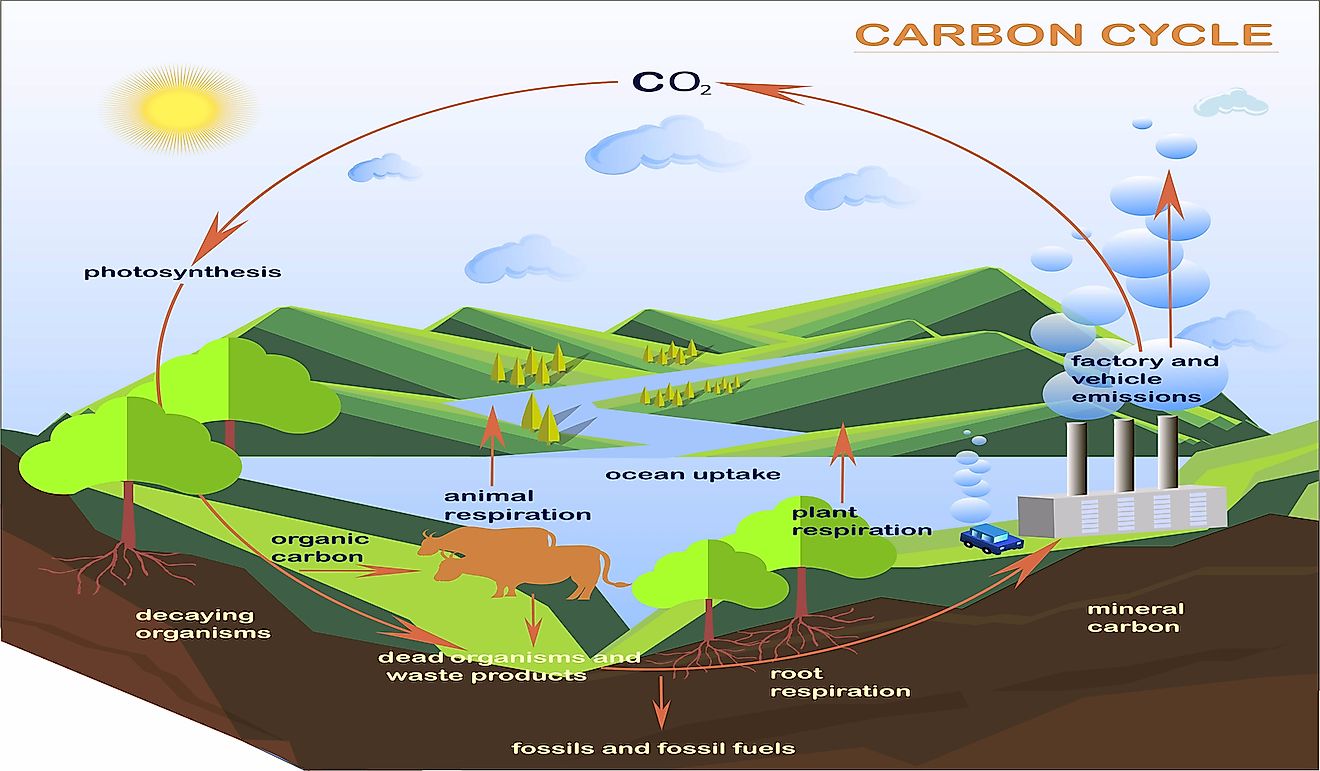
What Is The Carbon Cycle?
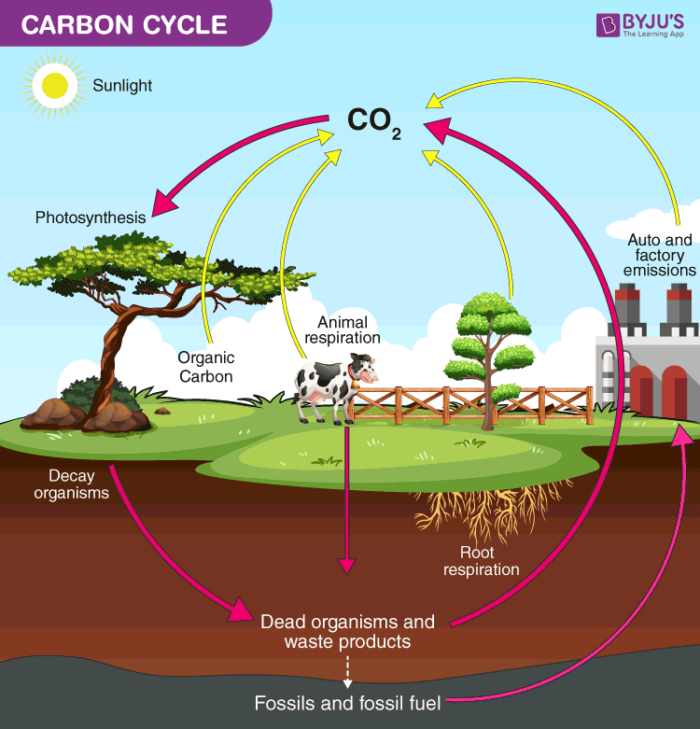
Carbon Cycle Definition, Process, Diagram Of Carbon Cycle

Carbon cycle Royalty Free Vector Image VectorStock
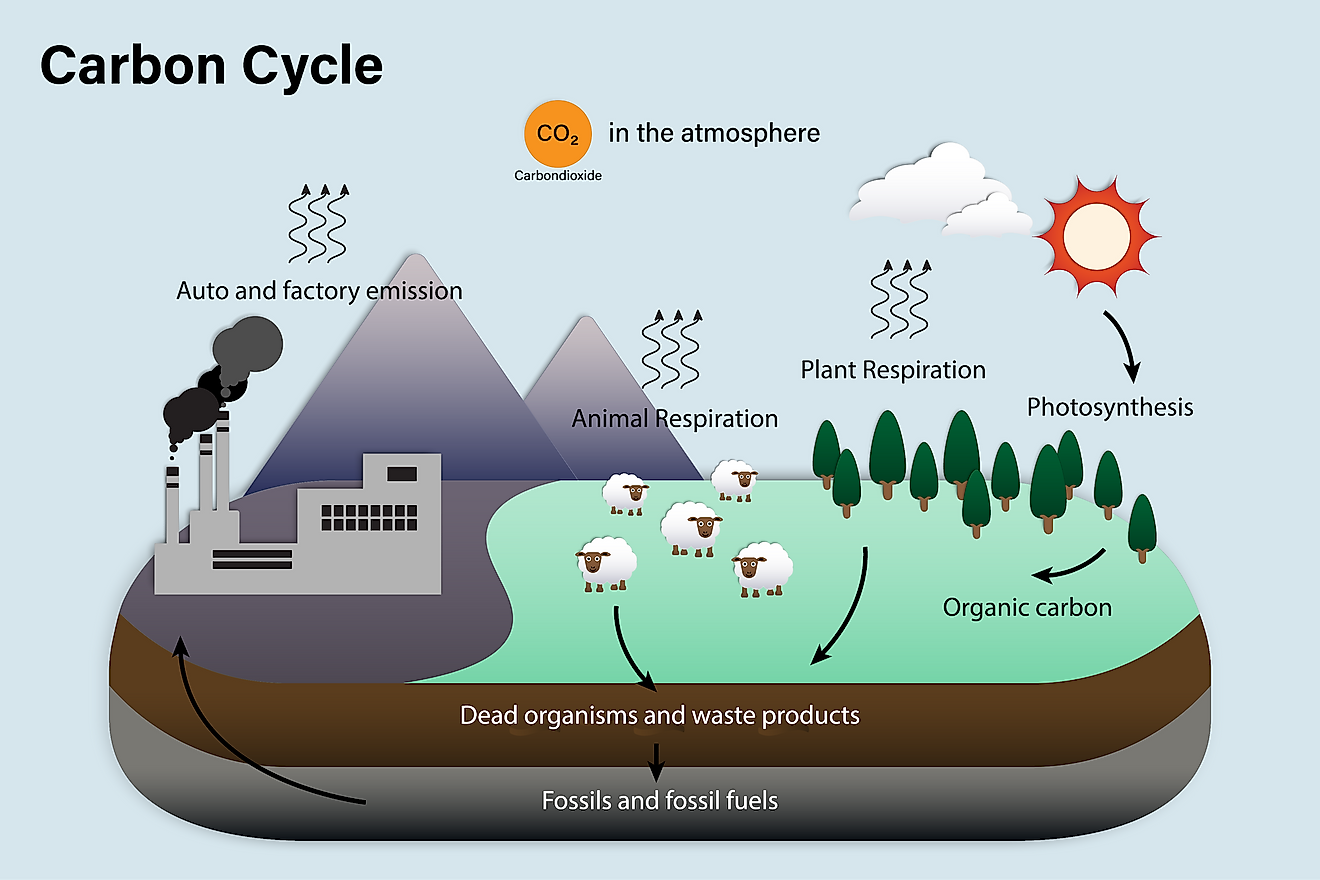
Carbon Cycle WorldAtlas

Carbon Cycle GLOBE.gov

Systems Thinking and the Carbon Cycle An Interactive Introduction to
The Carbon Cycle Farm Carbon Toolkit
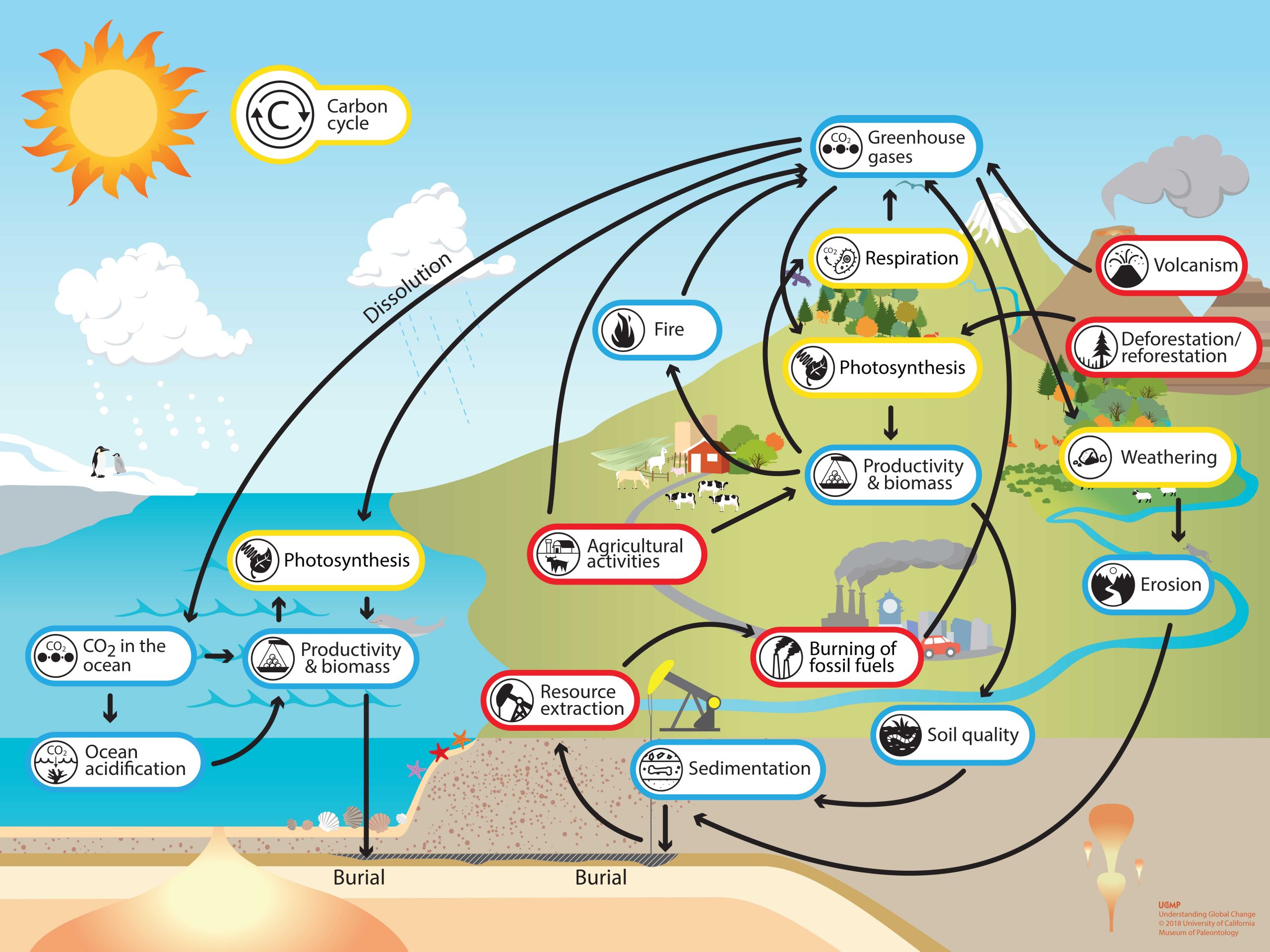
Carbon cycle Understanding Global Change

The Carbon Cycle UCAR Center for Science Education
There Are Arrows Pointing From Air Sea Gas Exchange, Human Emissions, And A Volcano Pointing Towards Carbon Dioxide In Atmosphere.
The Source Of The Carbon Found In Living Matter Is Carbon Dioxide (Co 2) In The Air Or Dissolved In Water.
© Inna Artanova/Getty Images Knowledge Of The Carbon Cycle Is Integral To Understanding How Chemistry Can Help Mitigate Climate Change
Kate Simonen The Edward And Mary Allen Lecture In Structural Design Presented With The Building T.
Related Post: