Extracellular Matrix Drawing
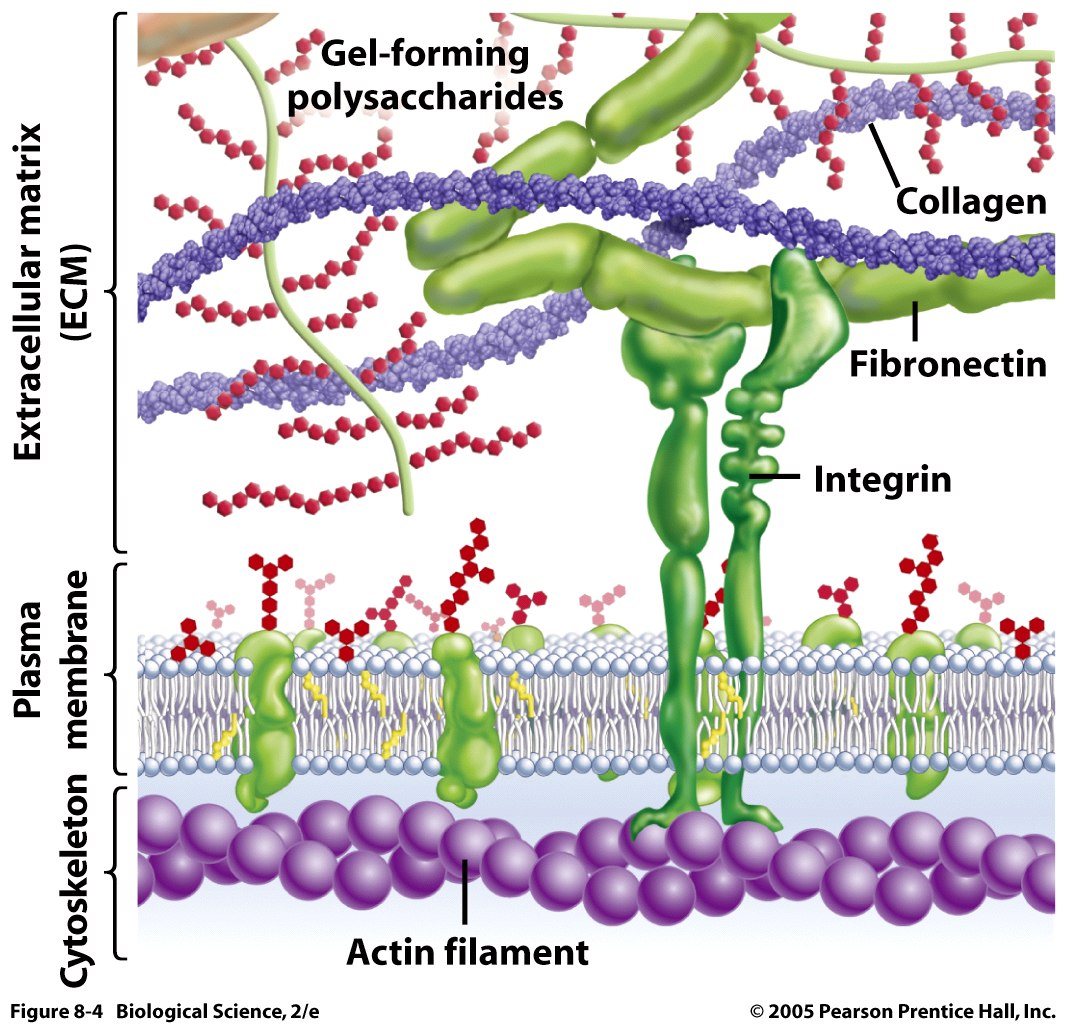
Extracellular Matrix Drawing - The extracellular matrix consists of a network of substances secreted by cells (figure 19.1). Accumulated knowledge clearly demonstrated over the last decade that ecm plays key regulatory roles since it orchestrates cell signaling, functions, properties. Blood clotting provides an example of the role of the extracellular matrix in cell communication. Web extracellular matrix is a general term for the extremely large proteins and polysaccharides that are secreted by some cells in a multicellular organism, and which acts as connective material to hold cells in a defined space. It can regulate a cell's behavior by communicating with a cell through integrins. Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) is a fundamental component of biological tissues. Most animal cells release materials into the extracellular space. Web extracellular matrix (ecm) presents in the muscle niche and is composed of proteins, polysaccharides , and rna etc., which plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis and regulating the development of skeletal muscle. The primary components of these materials are glycoproteins and the protein collagen. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Web the exact number of extracellular matrix macromolecules in the human body is unknown. The extracellular matrix consists of a network of substances secreted by cells (figure 19.1). Web extracellular matrix is a general term for the extremely large proteins and polysaccharides that are secreted by some cells in a multicellular organism, and which acts as connective material to hold. Web extracellular matrix (ecm) presents in the muscle niche and is composed of proteins, polysaccharides , and rna etc., which plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis and regulating the development of skeletal muscle. The type and composition of the ecm vary depending on several factors including the tissue and organ of the body. Examples include the cuticles of worms. The extracellular matrix consists of a network of substances secreted by cells (figure 19.1). Web extracellular matrix is a general term for the extremely large proteins and polysaccharides that are secreted by some cells in a multicellular organism, and which acts as connective material to hold cells in a defined space. I hope this helps and answers your question. Web. Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) is a fundamental component of biological tissues. The type and composition of the ecm vary depending on several factors including the tissue and organ of the body. Anchoring junctions mechanically attach cells (and their cytoskeletons) to. This dynamic structure has many roles in cellular adhesion, signaling, and overall cellular organization. Destruction of collagen fibers in. Extracellular matrix on cell surface receptors. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: It can regulate a cell's behavior by communicating with a cell through integrins. Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) is a fundamental component of biological tissues. Examples include the cuticles of worms and insects, the shells of mollusks, and, as. Anchoring junctions mechanically attach cells (and their cytoskeletons) to. Web we focus on the extracellular matrix of vertebrates, but the origins of the extracellular matrix are very ancient and virtually all multicellular organisms, make it; It influences a wide number of cellular processes including migration, wound healing and differentiation, all of which is of particular interest to researchers in the. Occluding junctions seal cells together in an epithelium in a way that prevents even small molecules from leaking from one side of the sheet to the other. Start practicing—and saving your progress—now: The primary components of these materials are glycoproteins and the protein collagen. Blood clotting provides an example of the role of the extracellular matrix in cell communication. Types. Proteins in the extracellular matrix, like the fibronectin molecules shown in green in the diagram above, can act as bridges between integrins and other extracellular. Web extracellular matrix is a general term for the extremely large proteins and polysaccharides that are secreted by some cells in a multicellular organism, and which acts as connective material to hold cells in a. Extracellular matrix on cell surface receptors. More direct applications of the extracellular matrix include its role in supporting growth and wound healing. This dynamic structure has many roles in cellular adhesion, signaling, and overall cellular organization. Web courses on khan academy are always 100% free. Types of extracellular matrix 3. This dynamic structure has many roles in cellular adhesion, signaling, and overall cellular organization. Destruction of collagen fibers in skin tissues. Proteins in the extracellular matrix, like the fibronectin molecules shown in green in the diagram above, can act as bridges between integrins and other extracellular. Animal tissue is not only composed of cells but also contains many types of. Two major classes of the ecms are known: Web the extracellular matrix (ecm) of hyaline cartilage is homogeneous and glassy, rich in in type ii collagen, proteoglycans such as aggrecan, and structural glycoproteins such as chondronectin. Loose connective tissue and the extracellular matrix fibers of extracellular matrix. Most animal cells release materials into the extracellular space. Web extracellular matrix (ecm) presents in the muscle niche and is composed of proteins, polysaccharides , and rna etc., which plays an important role in maintaining homeostasis and regulating the development of skeletal muscle. Anchoring junctions mechanically attach cells (and their cytoskeletons) to. Collectively, these materials are called the extracellular matrix. The extracellular matrix consists of a network of substances secreted by cells. Web since the extracellular matrix is thick and mineralized despite its water rich content, it has the additional function of keeping the cells in a tissue separate and physically distinct. This dynamic structure has many roles in cellular adhesion, signaling, and overall cellular organization. Web extracellular matrix in tissues are the supporting network of proteins that allow the cells of the tissue to function through binding together, dividing and differentiating. I hope this helps and answers your question. Web scientific medical anatomical 3d illustration extracellular matrix labeled infographic vector illustration scheme. Biological diagram with collagen fiber, fibronectin, phospholipid bilayer and cytoskeleton filaments. Extracellular matrix on cell surface receptors. Some of the key connectors are proteins called integrins , which are embedded in the plasma membrane.
Schematic representation of the extracellular matrix (ECM) components

Schematic overview of extracellular matrix and its major components

Extracellular matrix labeled infographic vector illustration scheme
Extra Cellular Matrix Is Critical to Neuroplasticity

(A) Schematic of the extracellular matrix. Cells lining ducts or blood

Illustration of Extracellular Matrix (ECM) molecules. The ECM is

Schematic representation of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Collagen

Extracellular Matrix Biochemistry Medbullets Step 1

Extracellular Matrix Proteins

4.8D Extracellular Matrix of Animal Cells Biology LibreTexts
More Direct Applications Of The Extracellular Matrix Include Its Role In Supporting Growth And Wound Healing.
Functions Such As Learning, Memory, Synaptogenesis, And Plasticity Are Regulated By Numerous Ecm Molecules.
Occluding Junctions Seal Cells Together In An Epithelium In A Way That Prevents Even Small Molecules From Leaking From One Side Of The Sheet To The Other.
Types Of Extracellular Matrix 3.
Related Post: