How To Draw Dense Irregular Connective Tissue
How To Draw Dense Irregular Connective Tissue - 842 views 2 years ago. Web learn to draw dense irregular connective tissue ( ct) histology diagram ( microscopic anatomy) mbbs histology slides 616 subscribers subscribe 2.2k views 2 years ago. Web 31k views 1 year ago. Examples include adipose, cartilage, bone, blood, and. Web dense irregular connective tissue is a type of dense connective tissue found widely dispersed throughout the body, particularly in areas where tension is applied from multiple different directions. Use the image slider below to learn how to use a microscope to identify and study dense irregular connective tissue on. As a consequence, it displays greater resistance to stretching. Web dense regular connective tissue comprises structures such as ligaments, tendons and aponeuroses, whilst dense irregular tissue is more widely distributed throughout the body. There are two major categories of dense connective tissue: Thick collagen fibers and bundles #2. It contains a high proportion of type i collagen fibers which, unlike in dense regular connective tissue, are randomly organized, forming an. [1] fibroblasts are the predominant cell type, scattered sparsely across the tissue. Thin elastic fibers (branching and anastomosing) #3. Thick collagen fibers and bundles #2. Some are solid and strong, while others are fluid and flexible. Use the image slider below to learn more about the characteristics of dense irregular connective tissue. #4 skin, h&e under the stratified squamous epithelium examined earlier is the dense irregular connective tissue of the dermis.its thick collagenous (type i) bundles stain intensely with eosin and can be seen to course in various directions. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which. Draw a restriction map that accounts for the results of this southern blot. Examples include adipose, cartilage, bone, blood, and. A few distinct cell types and densely packed fibers in a matrix characterize these tissues. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose. Thick collagen fibers and bundles #2. Web in this connective tissue collagenous fibers predominate. Use the image slider below to learn how to use a microscope to identify and study dense irregular connective tissue on. The outer layer, the epidermis, consists of stratified squamous epithelium. Web the skin consists of two distinct layers. Examples include adipose, cartilage, bone, blood, and. Thin elastic fibers (branching and anastomosing) #3. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose. This article will describe the cell types making up connective tissue as well as the histology and function of dense regular and dense irregular connective. [1] fibroblasts are the predominant cell type, scattered sparsely across the tissue. Blood vessels on the. In bone, the matrix is rigid and described as calcified because of the deposited calcium salts. Draw a restriction map that accounts for the results of this southern blot. Blood vessels on the sample connective tissue sample okay, now you might find out and identify these structures from the sample tissue sample. Web however, in previous problems involving restriction mapping,. Draw a restriction map that accounts for the results of this southern blot. Web the skin consists of two distinct layers. The outer layer, the epidermis, consists of stratified squamous epithelium. Dense connective tissue contains more collagen fibers than does loose connective tissue. The first 6 minutes of this video gives some hints and strategies for how to quickly identify. Web 31k views 1 year ago. #4 skin, h&e under the stratified squamous epithelium examined earlier is the dense irregular connective tissue of the dermis.its thick collagenous (type i) bundles stain intensely with eosin and can be seen to course in various directions. Fibrocytes in the densely packed collagen bundles #4. The first 6 minutes of this video gives some. Web the skin consists of two distinct layers. The first 6 minutes of this video gives some hints and strategies for how to quickly identify different connective tissue. Use the image slider below to learn how to use a microscope to identify and study dense irregular connective tissue on. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. The outer layer, the epidermis, consists of stratified squamous epithelium. Tendons connecting muscles to bone and ligaments connecting bone to bone are examples. Frank o'neill growgraymatter 33.8k subscribers subscribe 2.2k views 3 years ago tissues and histology. Web the cells of dense irregular connective tissue are fibrocytes which appear thin and dark cells with condensed nuclei scattered sparsely throughout the tissue. Use the image slider below to learn more about the characteristics of dense irregular connective tissue. Web supportive connective tissue —bone and cartilage—provide structure and strength to the body and protect soft tissues. Specialized connective tissue encompasses a number of different tissues with specialized cells and unique ground substances. The skin is composed of two main layers: Web dense connective tissue. Thick collagen fibers and bundles #2. A few distinct cell types and densely packed fibers in a matrix characterize these tissues. #4 skin, h&e under the stratified squamous epithelium examined earlier is the dense irregular connective tissue of the dermis.its thick collagenous (type i) bundles stain intensely with eosin and can be seen to course in various directions. The epidermis, made of closely packed epithelial cells, and the dermis, made of dense, irregular connective tissue that houses blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and other structures. Web some are classified as dense connective tissue proper and have a dense arrangement of extracellular protein fibers that give the tissue strength and toughness. Use the image slider below to learn how to use a microscope to identify and study dense irregular connective tissue on. The first 6 minutes of this video gives some hints and strategies for how to quickly identify different connective tissue. Beneath the dermis lies the hypodermis, which is composed mainly of loose. Tendons connecting muscles to bone and ligaments connecting bone to bone are examples of dense connective tissue proper.
Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Diagram Quizlet

Learn to make histological diagram of Dense irregular connective tissue

A2 Dense Irregular Connective Tissue Diagram Quizlet

21 How to Draw Dense Irregular Connective Tissue & Adipose fat

Dense connective tissue dense irregular and dense regular Connective

Histology Of Connective Tissues Lab

dense irregular collagenous connective tissue Diagram Quizlet

Dense irregular connective tissue Wikipedia

Connective Tissue Supports and Protects · Anatomy and Physiology
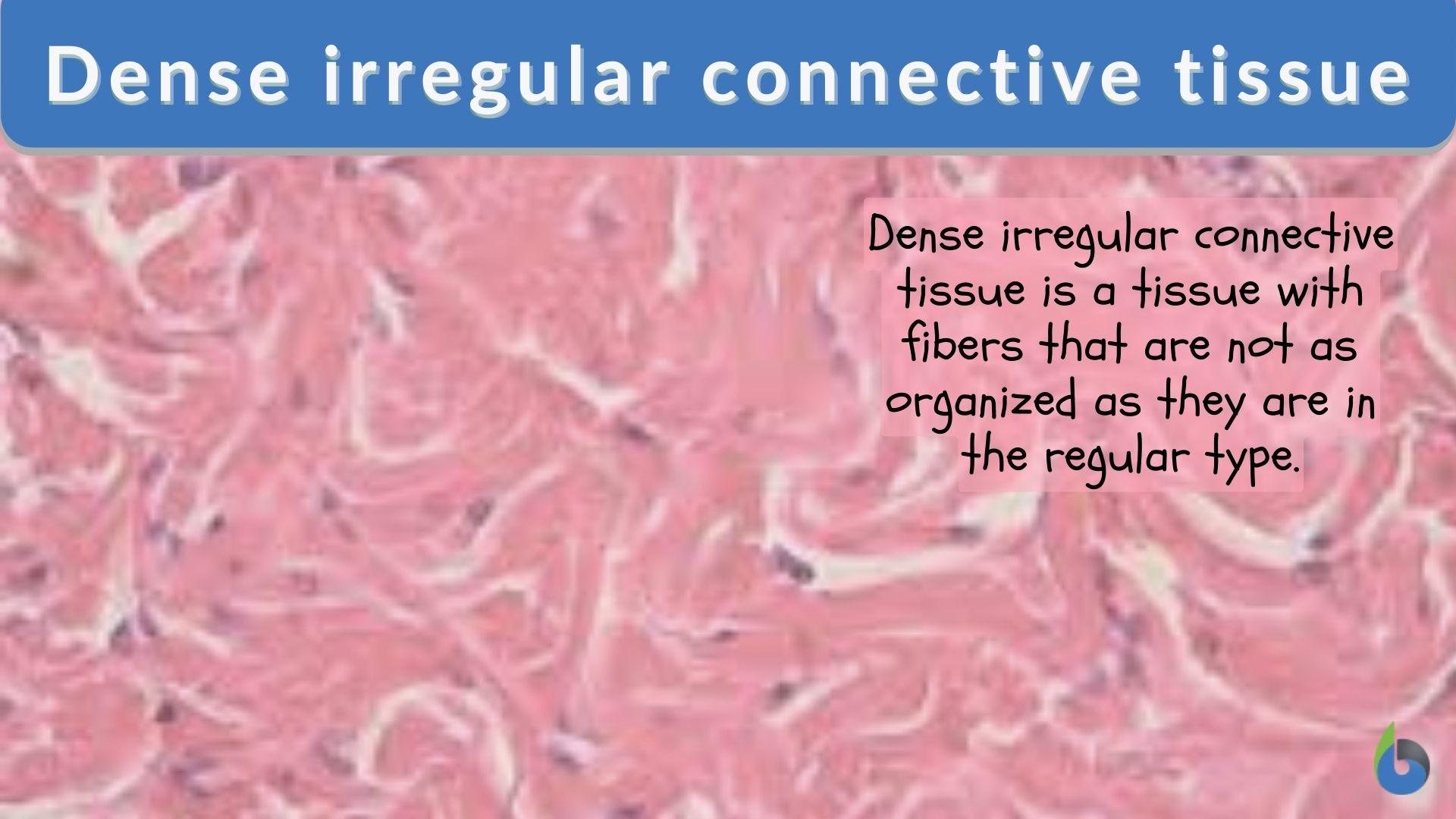
Dense irregular connective tissue Biology Online Dictionary
Blood Vessels On The Sample Connective Tissue Sample Okay, Now You Might Find Out And Identify These Structures From The Sample Tissue Sample.
Fibrocytes In The Densely Packed Collagen Bundles #4.
It Contains A High Proportion Of Type I Collagen Fibers Which, Unlike In Dense Regular Connective Tissue, Are Randomly Organized, Forming An.
There Are Two Major Categories Of Dense Connective Tissue:
Related Post: