How To Draw Orbital Diagram
How To Draw Orbital Diagram - Web how to draw orbital diagrams. In to circuitous graphic, an electron is represented by an arrow, while ampere box represents an atomic orbital. Web valence bond theory vbt. This is also due to the history when they were discovered. Web orbital diagrams are a pictorial description of electrons in an atom. Valence bond theory (vbt) in simple terms explains how individual atomic orbitals with an unpaired electron each, come close to each other and overlap to form a molecular orbital giving a covalent bond. Simple cubic unit cell 2m. Web orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Face centered cubic unit cell 2m. Body centered cubic unit cell 2m. These orbitals are filled with electrons (the amount of electrons depends on which element you are looking at). Web a molecular orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule (two atoms) varies in the number of electrons. In order to figure out where electrons go in an atom we have to follow 3 main rules. Web. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. Web a p orbital along the y axis is labeled p y and one along the z axis is a p z orbital. Repeat this process for the 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, and 4s orbitals, placing the appropriate number of arrows to represent the electrons. Web a molecular orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule (two atoms) varies in the number of electrons. Body centered cubic unit cell 2m. We start with a single hydrogen atom (atomic number 1), which consists of one proton and one electron. Web valence bond theory vbt. Web typically, they only show the outermost electrons. Web the orbital diagram or orbital notation simply represents the arrangement of electrons in different orbsitals of to atom. Hund's rule and orbital filling diagrams Web orbital diagrams are pictorial representations of the electron configuration, showing the individual orbitals and the pairing arrangement of electrons. Below are dot density diagrams, boundary surface diagrams, and a rotating image. Web orbital diagrams. The first one being the auf bau principle, the auf bau principle states that each electron occupies the lowest energy orbital available. Valence bond theory (vbt) in simple terms explains how individual atomic orbitals with an unpaired electron each, come close to each other and overlap to form a molecular orbital giving a covalent bond. Web in this article, we. Determine the total number of valence electrons in the he 2 2 + ion. Web orbital diagrams use the same basic format, but instead of numbers for the electrons, they use ↑ and ↓ arrows, as well as giving each orbital its own line, to represent the spins of the electrons too. This is done by first determining the subshell. Web the orbital diagram or orbital notation simply represents the arrangement of electrons in different orbsitals of to atom. This article will explore the basics of how to draw each type of diagram, and important rules to follow in their construction. The first one being the auf bau principle, the auf bau principle states that each electron occupies the lowest. Orbital diagrams are a visual way to show where the electrons are located within an atom. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules: Web a molecular orbital diagram for a diatomic molecule (two atoms) varies in the number of electrons. Heating and cooling curves 14m. That's the number of valence electrons on. Web orbital diagrams use the same basic format, but instead of numbers for the electrons, they use ↑ and ↓ arrows, as well as giving each orbital its own line, to represent the spins of the electrons too. Molecular orbital diagrams are complex, involving two additional orbitals, electronegativity, atomic symmetries and atomic energies. Web how to draw orbital diagrams. This. And then fill the electrons in empty orbital boxes using three rules. Atomic, ionic, and molecular solids 5m. Face centered cubic unit cell 2m. Web on this article, we willing discuss whole to different rules and principles of filling electrons in an atomic orbital diagram, followed the plenty of examples for drawing an oscillated charts or orbital style configuration. Although. Answer • count the valence electrons on the molecule. Web typically, they only show the outermost electrons. Web orbital diagrams use the same basic format, but instead of numbers for the electrons, they use ↑ and ↓ arrows, as well as giving each orbital its own line, to represent the spins of the electrons too. That's the number of valence electrons on. Web this chemistry video tutorial provides a basic introduction into orbital diagrams and electron configuration. And then fill the electrons in empty orbital boxes using three rules. Although more complex, these diagrams reveal a more realistic case for bonding, allowing electrons to travel about a molecule, rather than in. Imagine shells around the nucleus, that get bigger and bigger. Web how to draw orbital diagrams. Web in this article, we leave discuss all the different rules and corporate of filling electrons in an atomic oscillated diagram, followed by plenty of examples to drawing certain orbital diagram oder orbital notation configuration. Web orbital diagrams orbital diagrams help visualize which orbitals the electrons in an atom are the basics of orbital diagrams there are different types of orbitals, that all have different energy levels. Web an orbital is a space where a specific pair of electrons can be found. Hund's rule and orbital filling diagrams It explains how to write the orbital diagram notation (with arrows) of an element. Overlapping atomic orbitals produce molecular orbitals. Orbital diagrams must follow 3 rules:
How to Draw Molecular Orbital Diagrams (MO DIAGRAMS) Explanation YouTube
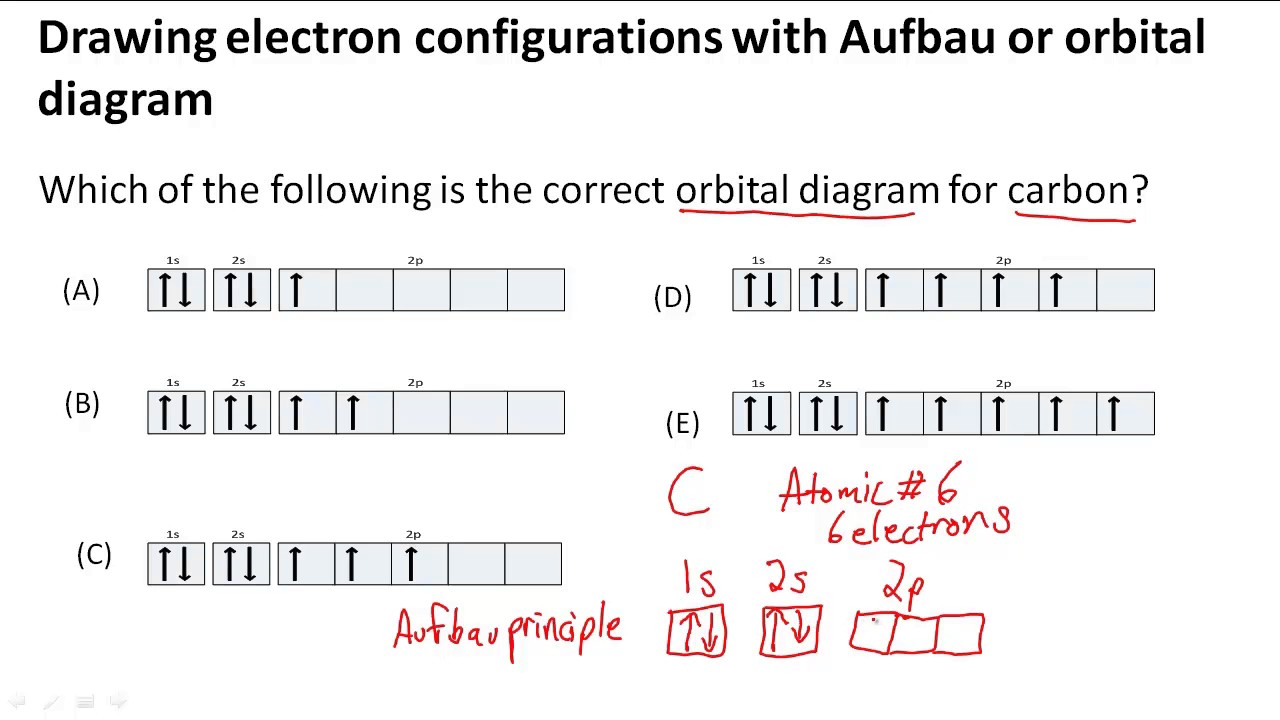
Drawing electron configurations with Aufbau/orbital diagram YouTube

Atomic orbitals explained polizhuge
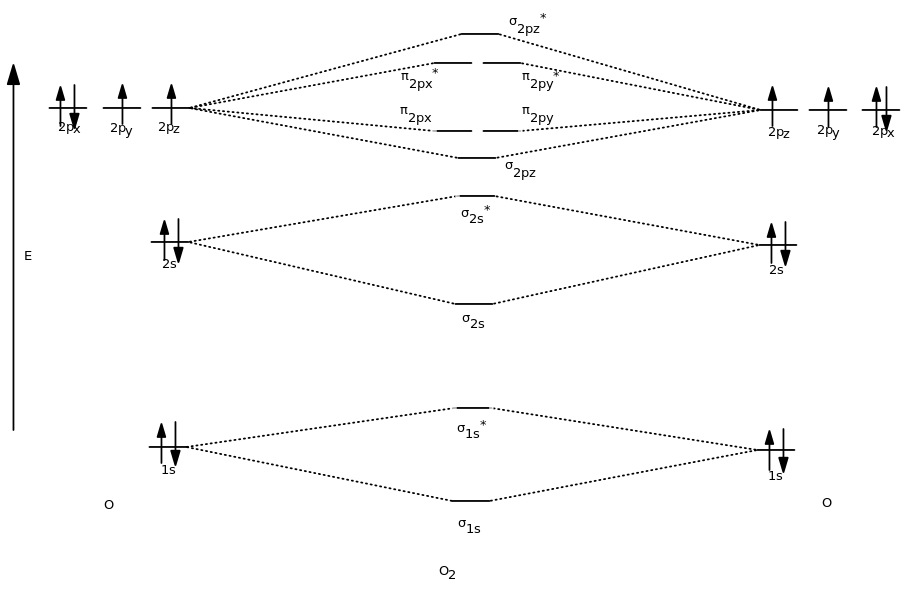
Drawing Atomic and Molecular Orbitals Diagrams for Molecules Organic

Molecular Orbital Diagrams simplified by Megan Lim Medium

Shapes of Atomic Orbitals — Overview & Examples Expii

Drawing Orbital Diagrams

Orbital Diagrams — Overview & Examples Expii

Orbital Diagrams — Overview & Examples Expii
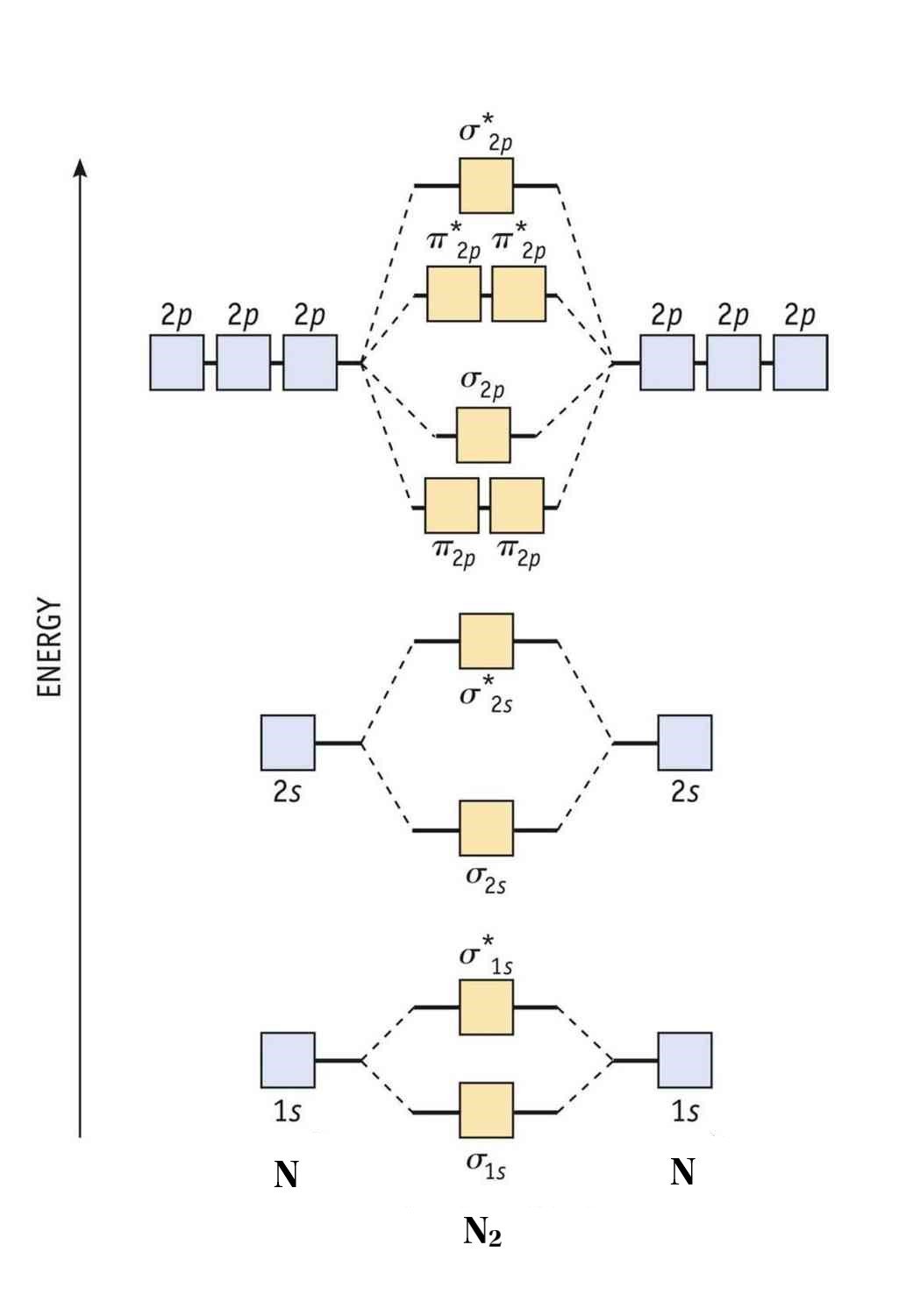
8 Drawing Molecular Orbital Diagrams — Flux Science
This Article Will Explore The Basics Of How To Draw Each Type Of Diagram, And Important Rules To Follow In Their Construction.
We Start With A Single Hydrogen Atom (Atomic Number 1), Which Consists Of One Proton And One Electron.
Face Centered Cubic Unit Cell 2M.
Molecular Orbital Diagrams Are Complex, Involving Two Additional Orbitals, Electronegativity, Atomic Symmetries And Atomic Energies.
Related Post: