How To Draw Position Time Graph From Velocity Time Graph
How To Draw Position Time Graph From Velocity Time Graph - Velocity from position time graphs. The final position will be the initial position plus the area under the velocity versus time graph. A keyframe marks the point in time where you specify a value, such as spatial position, opacity, or audio volume. , then the graph will be a curve. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c) throughout the interval. Web repeat step 4, stopping the times at the distances of 1.0 m, 1.5 m, 2.0 m, 2.5 m, and 3.0 m from the bottom of the ramp. Web the slope of a position graph represents the velocity of the object. Time change as they adjust to match the motion shown on the velocity vs. A steeper slope indicates higher velocity, while a gentle slope indicates slower velocity. The camera took one frame every 2 s. Web in premiere pro, effect properties can be animated by assigning keyframes to them. (change in position) / (change in time). Using the graph to determine displacement, distance, average velocity, average speed, instantaneous velocity, and instantaneous speed. Repeat steps 4 through 6, with different people taking on the roles of experimenter, timer, and recorder. Watch how the graphs of position. Time graph to determine position. We know that v = d / t. 181k views 8 years ago global math institute resource. A keyframe marks the point in time where you specify a value, such as spatial position, opacity, or audio volume. Given a position vs time graph, draw a velocity vs time graph (constant velocities only) The final position will be the initial position plus the area under the velocity versus time graph. Average speed and average velocity from graphs. Time graph for two bicycles, a and b.(b) which bicycle has the larger accel. Time graph of the ball’s motion. The camera took one frame every 2 s. Time graph for two bicycles, a and b.(b) which bicycle has the larger accel. Time graph to determine position. So you have 2 seconds at 4 m/s, and 1 second at, on average, 3 m/s. Average velocity equals the change in position (represented by δd) divided by the corresponding change in time (represented by δt): This can be done by. So you have 2 seconds at 4 m/s, and 1 second at, on average, 3 m/s. Web how to read a position vs. Time graph for two bicycles, a and b.(a) identify any instant at which the. To create a change in a property over time, you set at least two keyframes—one keyframe for the value at the beginning of. Web it is the velocity at 2.5 seconds, of course. Average speed and average velocity from graphs. Given a position vs time graph, draw a velocity vs time graph (constant velocities only) • position or displacement time and vel. Velocity from position time graphs. Average velocity equals the change in position (represented by δd) divided by the corresponding change in time (represented by δt): Figure ex1.18 shows the motion diagram of a drag racer. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c) throughout the interval. Web in premiere pro, effect properties can be animated by assigning keyframes to them. Time graph by sliding. A keyframe marks the point in time where you specify a value, such as spatial position, opacity, or audio volume. Time graph for two bicycles, a and b.(b) which bicycle has the larger accel. So the value of the slope at a particular time represents the velocity of the object at that instant. Web the slope of a position graph. We know that v = d / t. Time graph by sliding the points up or down. Next position displacement velocity acceleration graph: A steeper slope indicates higher velocity, while a gentle slope indicates slower velocity. Web the slope of a position graph represents the velocity of the object. Average speed and average velocity from graphs. As the graph shows, the velocity is constant (c) throughout the interval. Time change as they adjust to match the motion shown on the velocity vs. Watch how the graphs of position vs. Average velocity equals the change in position (represented by δd) divided by the corresponding change in time (represented by δt): Given a position vs time graph, draw a velocity vs time graph (constant velocities only) Time graph for two bicycles, a and b.(a) identify any instant at which the. Velocity from position time graphs. 181k views 8 years ago global math institute resource. Figure ex1.18 shows the motion diagram of a drag racer. Web represent and calculate the distance traveled by an object, as well as the displacement, the speed and the velocity of an object for different problems. Web it is the velocity at 2.5 seconds, of course. Web how to read a position vs. Representations include data tables, distance versus time graphs, position versus time graphs, motion diagrams and their mathematical representations. The final position will be the initial position plus the area under the velocity versus time graph. And then you add them to the initial position. Watch how the graphs of position vs. Time graph of the ball’s motion. This can be done by calculating the derivative in the context of calculus. So the value of the slope at a particular time represents the velocity of the object at that instant. Time graph for two bicycles, a and b.(b) which bicycle has the larger accel.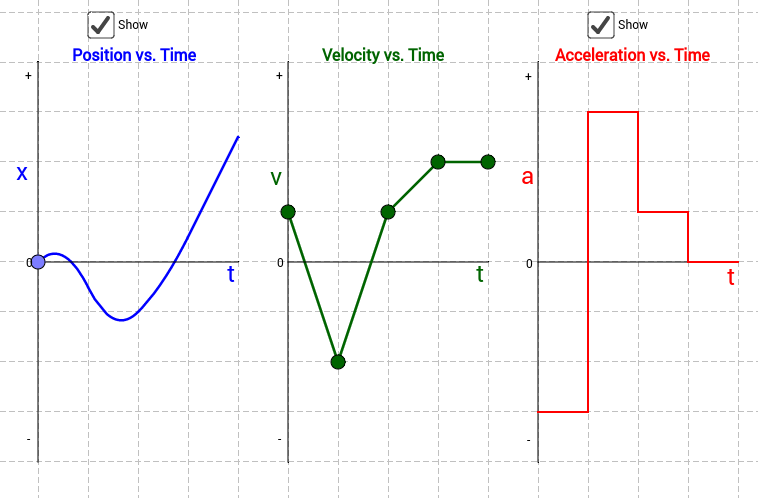
Position, Velocity, and Acceleration vs. Time Graphs GeoGebra

Velocity Time Graph Meaning of Shapes Teachoo Concepts

CSEC Physics How to Draw a Velocity Time Graph (VTG) Junior Roberts
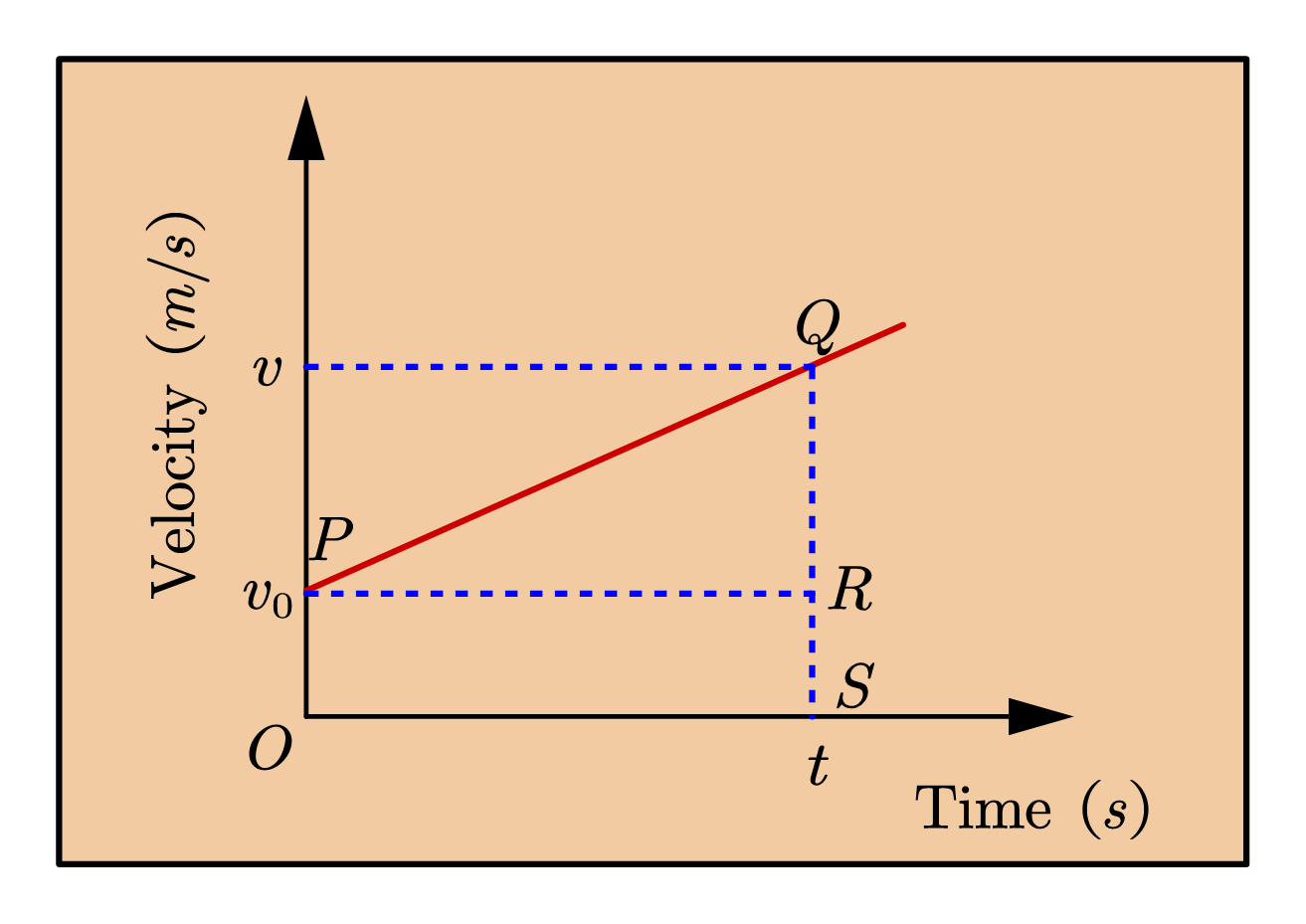
What is Velocity time graph? physicscatalyst's Blog

How to calculate velocity from a position vs time graph YouTube
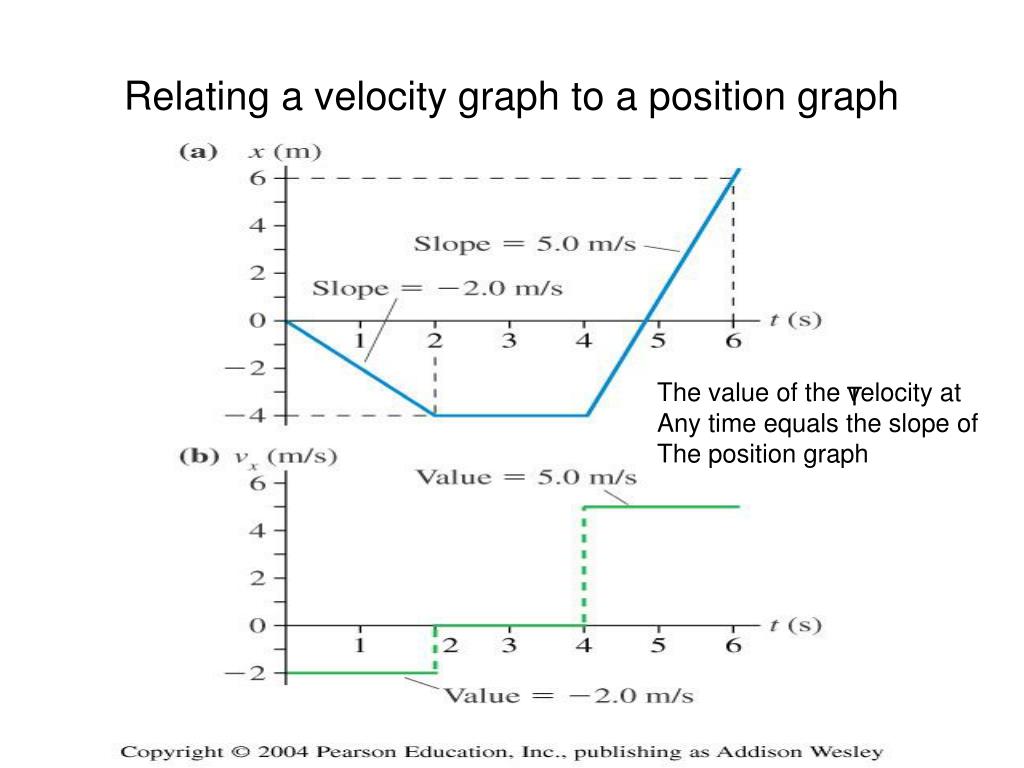
PPT Chapter 2 Kinematics PowerPoint Presentation ID762189
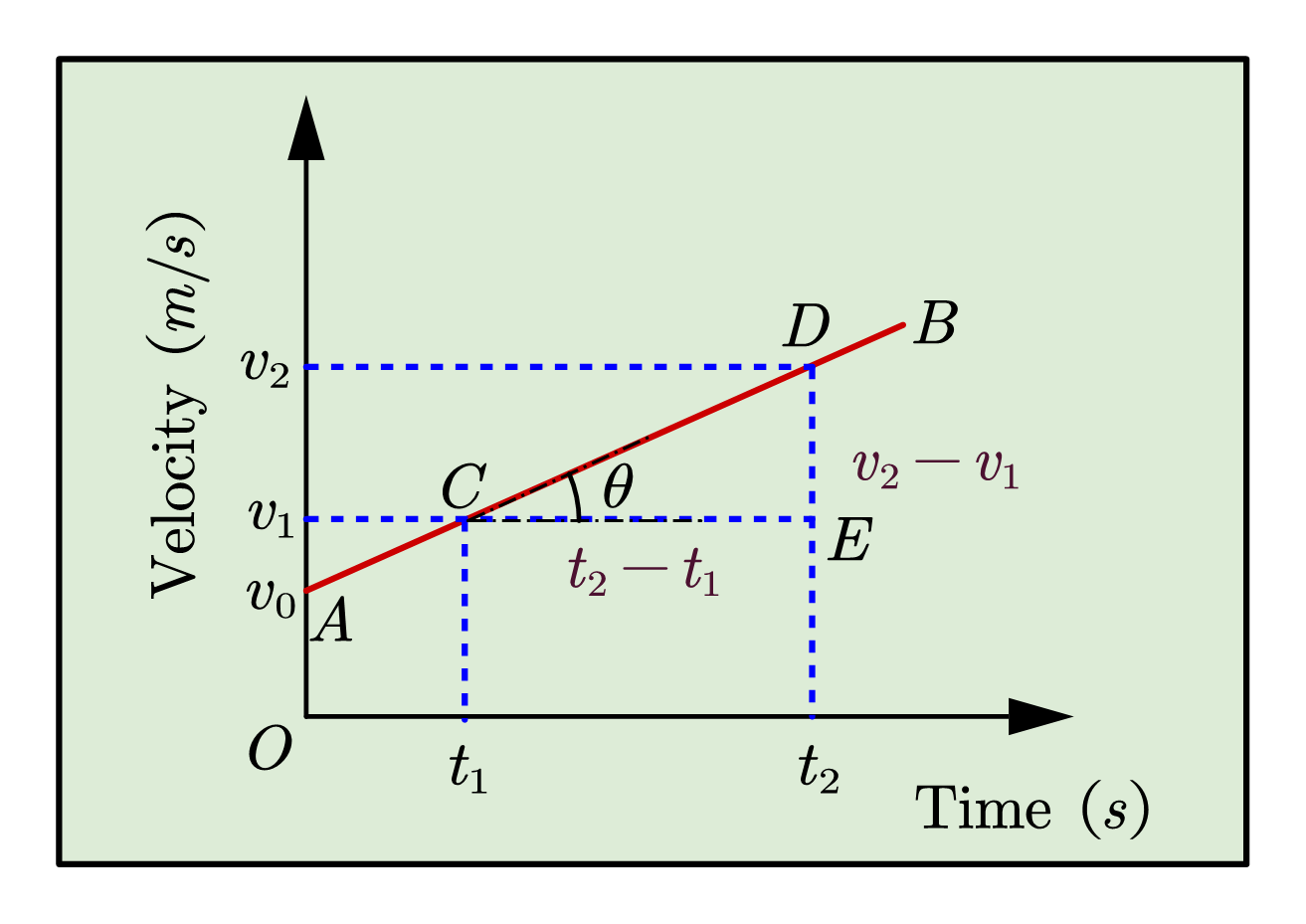
What is Velocity time graph? physicscatalyst's Blog
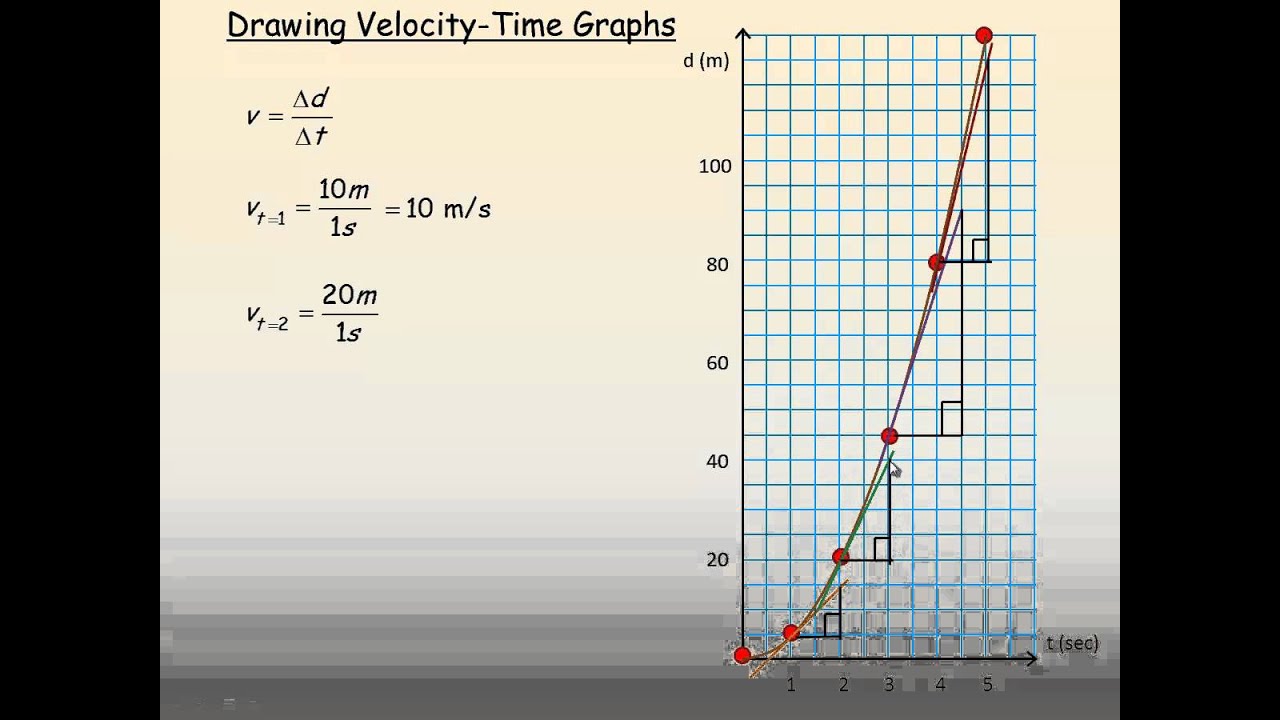
Drawing VelocityTime Graphs YouTube

Velocity time graphs (Video) PhysicsTube

Velocity Time Graph Meaning of Shapes Teachoo Concepts
The Formula For Calculating Slope Is Rise Over Run:
Adjust The Initial Position And The Shape Of The Velocity Vs.
Time Graph To Determine Velocity, We Can Use A Velocity Vs.
• Position Or Displacement Time And Vel.
Related Post: