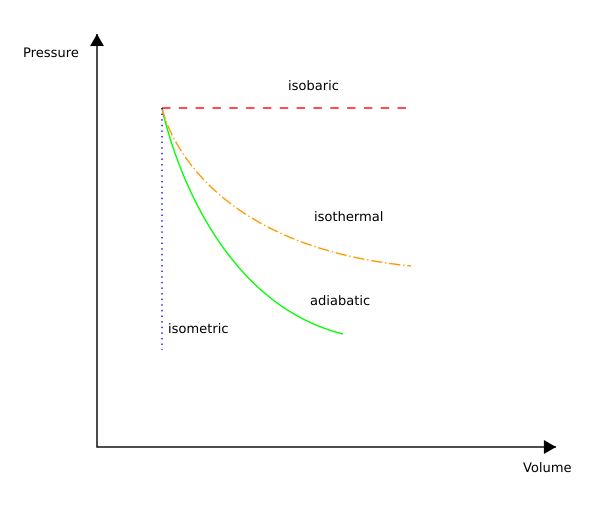
How To Draw Pv Diagram
How To Draw Pv Diagram - Pumping work is negative because it’s using energy from the engine to push exhaust gases out of the cylinders and draw fresh air during intake. W = − area on pv graph. Invent new logos, comic strips, and photorealistic scenes right in the chat. ∆u = 3 2 nr∆t. There are three types of thermodynamic processes you should know: Web on the figure we show two types of plots that are used to describe changes of state. Web learn what pv diagrams are and how to use them to find the change in internal energy, work done, and heat. Identify signs that say something about the process. Volume graph for a given temperature, by choosing a temperature and then using the volume slider to cover the full range of volumes. An isothermal process is all about keeping the temperature constant, while an isometric process maintains a constant volume. Select the number of points in the cycle (3 or 4), and then choose which type of process connects each point. Volume graph for a given temperature, by choosing a temperature and then using the volume slider to cover the full range of volumes. Consider a gas sealed in a container with a tightly fitting yet movable piston as seen. Volume was traced by a plate moving with the piston, while pressure was traced by a pressure gauge whose indicator moved at right angles to the piston. A process performed at constant temperature is called an isothermal process. How a pv diagram is drawn for a 4 stroke internal combustion engine; Volume graph for a given temperature, by choosing a. ∆u = 3 2 nr∆t. Select the number of points in the cycle (3 or 4), and then choose which type of process connects each point. In the first, the volume remains constant at 0.200 m^3 and the pressure increas. For gasoline atmospheric engines, due to intake air throttling, the pumping losses. Pumping work is negative because it’s using energy. Click on close cycle to. Web instructions this simulation calculates the net work done by a closed cycle. (b) calculate the work d. W = − area on pv graph. Volume was traced by a plate moving with the piston, while pressure was traced by a pressure gauge whose indicator moved at right angles to the piston. Click on close cycle to. A gas undergoes two processes. You can also sketch a pressure vs. Web learn what pv diagrams are and how to use them to find the change in internal energy, work done, and heat. Web overview of the types of thermodynamic processes and how they look in a pv diagram.subscribe: Web overview of the types of thermodynamic processes and how they look in a pv diagram.subscribe: Q = ∆u + w = nc∆t Consider a gas sealed in a container with a tightly fitting yet movable piston as seen below. You can bring your ideas to life with our most capable image model, dall·e 3. In addition, the processes plotted. A gas undergoes two processes. An isothermal process is all about keeping the temperature constant, while an isometric process maintains a constant volume. The pv diagram, then called an indicator diagram, was developed in 1796 by james watt and his employee john southern. You can bring your ideas to life with our most capable image model, dall·e 3. Web understand. Web on the figure we show two types of plots that are used to describe changes of state. You can bring your ideas to life with our most capable image model, dall·e 3. You can also sketch a pressure vs. Web understand the meaning of the pv diagram; W = − area on pv graph. Web on the figure we show two types of plots that are used to describe changes of state. In addition, the processes plotted on pv diagrams only work for a closed system (in this case the ideal gas), so there is no. For gasoline atmospheric engines, due to intake air throttling, the pumping losses. The first step is to understand. The first step is to understand for which thermodynamic process we are drawing a pv diagram. Invent new logos, comic strips, and photorealistic scenes right in the chat. A process performed at constant temperature is called an isothermal process. In the first, the volume remains constant at 0.200 m^3 and the pressure increas. W = ∫ f · ds =. Web learn what pv diagrams are and how to use them to find the change in internal energy, work done, and heat. Click on close cycle to. Web understand the meaning of the pv diagram; Web this physics video tutorial provides a basic introduction into pv diagrams. A pencil was used to draw the diagram. W = ∫ f · ds = ∫ p dv. Select the number of points in the cycle (3 or 4), and then choose which type of process connects each point. Pumping work is negative because it’s using energy from the engine to push exhaust gases out of the cylinders and draw fresh air during intake. For gasoline atmospheric engines, due to intake air throttling, the pumping losses. The first step is to understand for which thermodynamic process we are drawing a pv diagram. Two moles of an ideal gas are heated at constant pressure from t = 27°c to t = 107°c. Web thermo drawing t v and p v diagrams. A process performed at constant temperature is called an isothermal process. In the first, the volume remains constant at 0.200 m^3 and the pressure increas. In addition, the processes plotted on pv diagrams only work for a closed system (in this case the ideal gas), so there is no. ∆u = 3 2 nr∆t.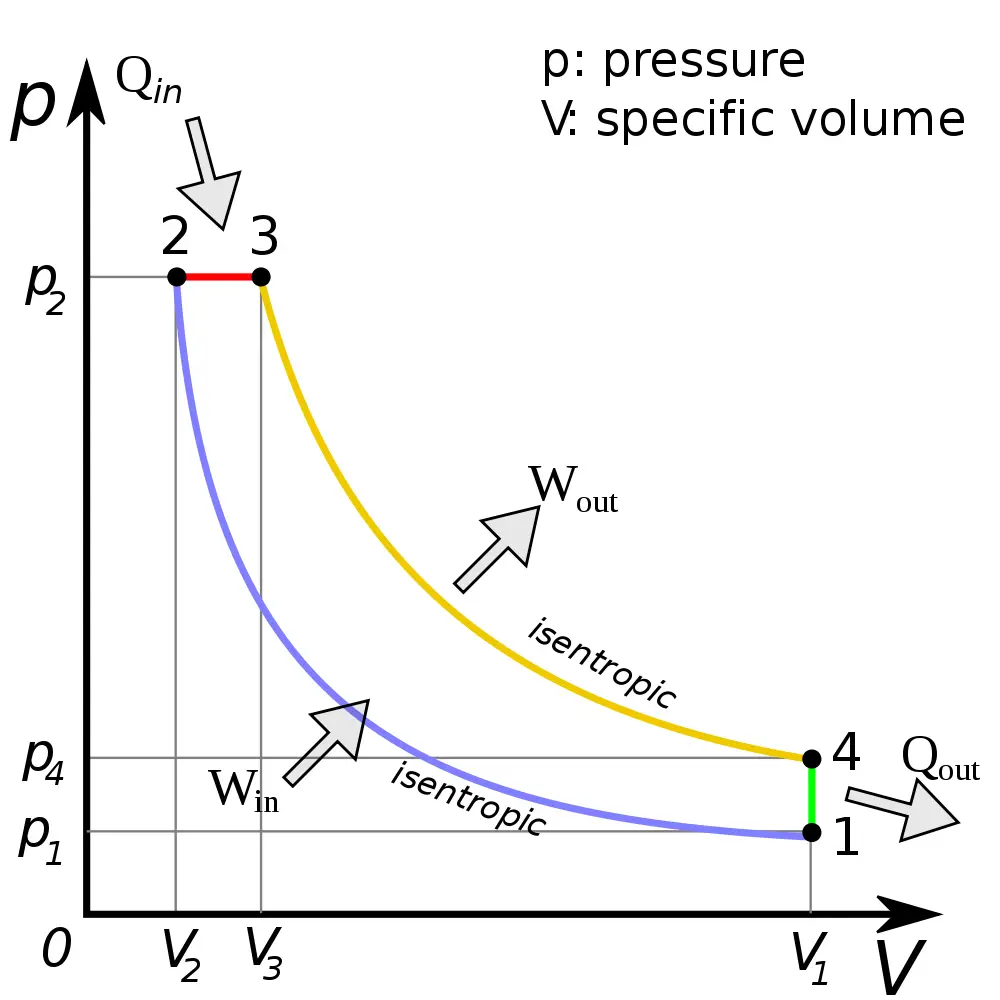
Diesel Cycle Process, PV Diagram, Efficiency with Derivation
![[Solved] How to draw this PV graph? 9to5Science](https://i.stack.imgur.com/mvjJ3.png)
[Solved] How to draw this PV graph? 9to5Science
Draw the PV diagram and the TS diagram for the

pv* diagram of real nonpolar fluid with its isotherms. Download

The pressurevolume (pV) diagram and how work is produced in an ICE x
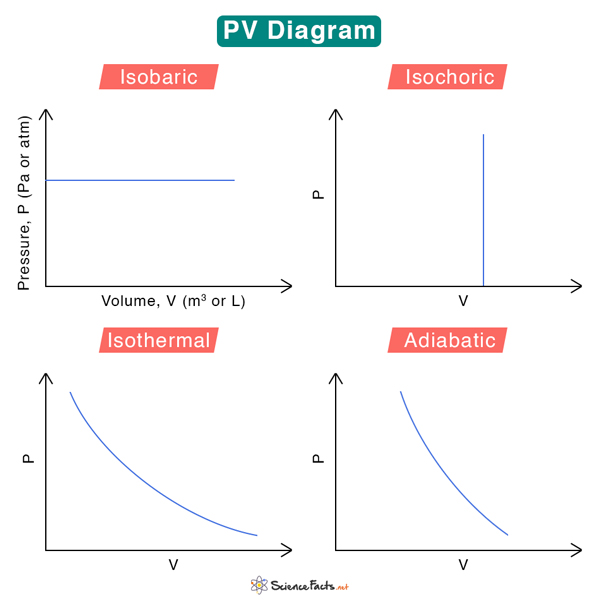
Pv Diagram Constant Volume
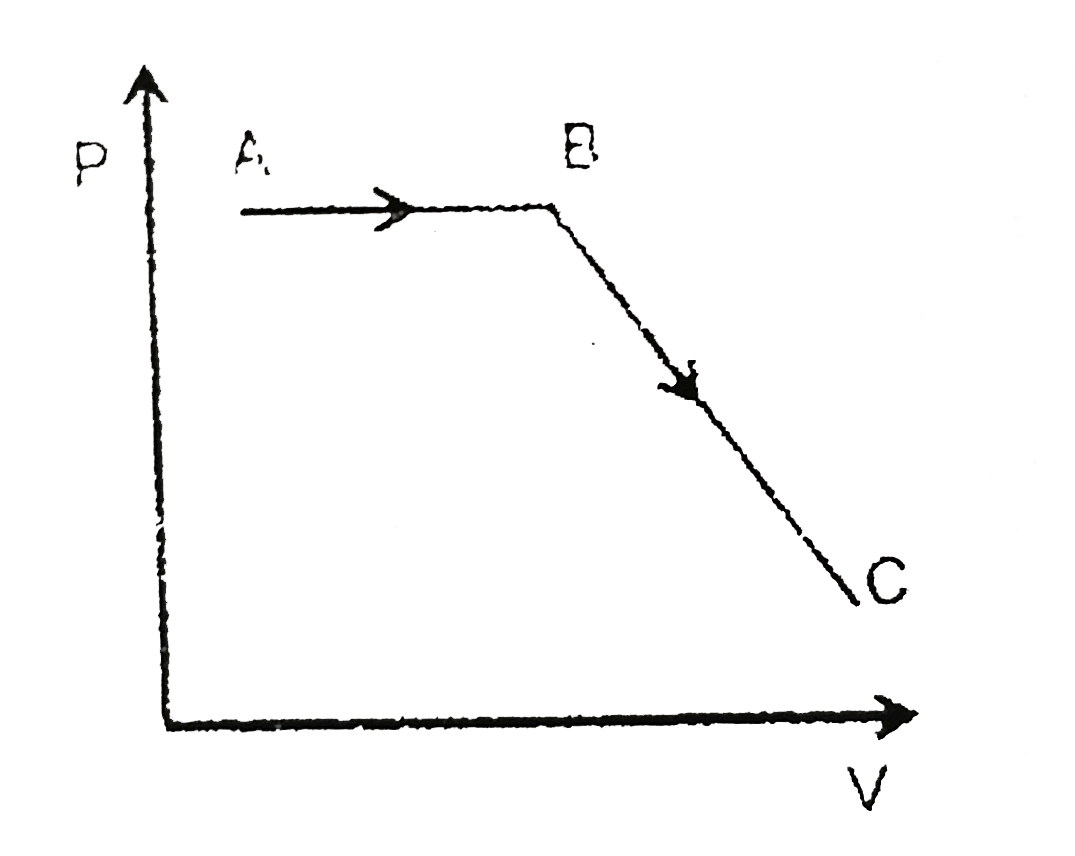
Draw pV diagram of reversible process.

pv diagram for a pure substance Download Scientific Diagram
Understanding the PressureVolume Diagrams — Omnia MFG
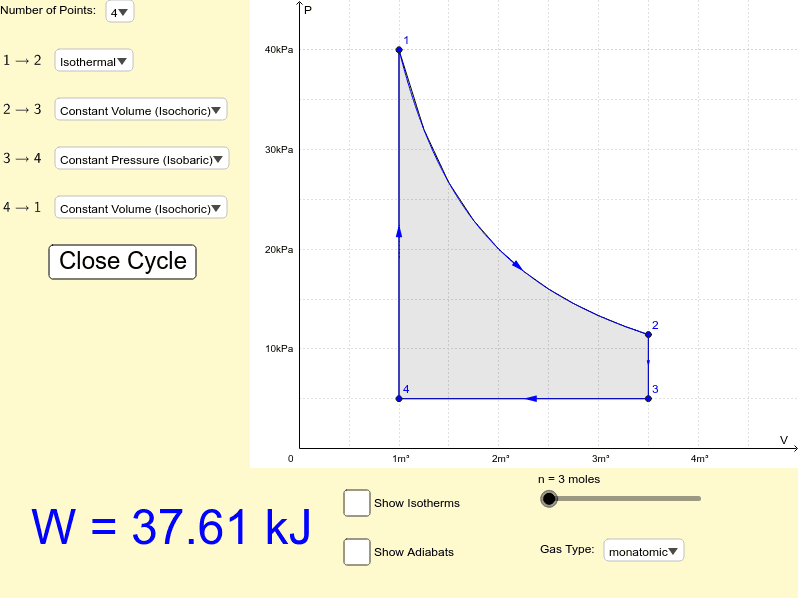
PV Diagram and Work GeoGebra
See What Happens When The Temperature Of The Ideal Gas Or The Volume Is Changed (At Constant Temperature).
Volume Graph For A Given Temperature, By Choosing A Temperature And Then Using The Volume Slider To Cover The Full Range Of Volumes.
(B) Calculate The Work D.
Web Instructions This Simulation Calculates The Net Work Done By A Closed Cycle.
Related Post: