How To Draw The Conjugate Base Of An Acid
How To Draw The Conjugate Base Of An Acid - Write the formula of the conjugate. What is the conjugate acid of each of the following? If we compare acetic acid to our next compound, this is chloroacetic acid. Remove a hydrogen atom from the acid given. Web 📗 need help with chemistry? Base + acid → conj a + conj b. Add a unit of negative charge to the molecule. H2so4 +h2o hso− 4 + h3o+. Web let's draw the conjugate base for acetic acid. All bases have a conjugate acid. The parent acid and its conjugate base (\(ch_3co_2h/ch_3co_2^−\)) and; It becomes the hydrogen sulfite ion ( hso− 4 ) which is the. The single bond is active by default. If we compare acetic acid to our next compound, this is chloroacetic acid. Web in the reverse reaction, \(h_3o^+\) is the acid that donates a proton to the acetate ion, which. The single bond is active by default. For example, if you have a mixture of benzoic acid and propylbenzene: This is most easily seen when they dissociate in water: Write the formula for the conjugate acid of the base nh2ch3. Web view the full answer. Web let's draw the conjugate base for acetic acid. For example, if you have a mixture of benzoic acid and propylbenzene: Notice we now have a chlorine attached to this carbon. Draw the molecule on the canvas by choosing buttons from the tools (for bonds), atoms, and advanced template toolbars. Draw the conjugate base of ch_3ch_2nh_2. For hydrochloric acid (hcl), this reaction becomes: We see that hco₃⁻ becomes h₂co₃. Now i didn't draw on lone pairs of electrons for. All acids have a conjugate base. Let us take the example of bicarbonate ions reacting with water to create carbonic acid and hydronium ions. The parent base and its conjugate acid (\(h_3o^+/h_2o\)). (1) donation of a proton by an acid, and (2) acceptance of a proton by a base. Web it's basically the same way as any other molecule. In this example, sulfuric acid ( h2so4 ) is an acid because it donates h+ to the water. Web in the reverse reaction, \(h_3o^+\) is. Acids donate h+ when they react. For example, if you have a mixture of benzoic acid and propylbenzene: For hydrochloric acid (hcl), this reaction becomes: Draw both the conjugate acid and conjugate base of the acid/base reaction shown below. What is the conjugate acid of each of the following? This is most easily seen when they dissociate in water: Base + acid → conj a + conj b. Vocabulary for finding the conjugate of an acid. Thus nh 3 is called the conjugate base of nh 4 +, and nh 4 + is the conjugate acid of nh 3. (1) donation of a proton by an acid, and (2). Draw the conjugate base of ch_3ch_2nh_2. It also shows you how to identify conjugate. The species formed from a base when it accepts a proton from an acid. The species formed from an acid when it donates a proton to a base. Notice we now have a chlorine attached to this carbon. (water served as the base in the acid example and as the acid in the base example [ amphiprotic ]). The parent acid and its conjugate base (\(ch_3co_2h/ch_3co_2^−\)) and; Web in the reverse reaction, \(h_3o^+\) is the acid that donates a proton to the acetate ion, which acts as the base. Any pair of molecules or ions that can be. The species formed from an acid when it donates a proton to a base. Vocabulary for finding the conjugate of an acid. This is most easily seen when they dissociate in water: The single bond is active by default. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl. Hcl + h 2 o ↔ cl − + h 3 o + here, the chloride anion,. (water served as the base in the acid example and as the acid in the base example [ amphiprotic ]). If acetic acid donates this proton, then the electrons in magenta are left behind on the oxygen, so the conjugate base would have a carbon double bonded to an oxygen here with two lone pairs of electrons. Remove a hydrogen atom from the acid given. Any pair of molecules or ions that can be interconverted by transfer of a proton. Web in the reverse reaction, \(h_3o^+\) is the acid that donates a proton to the acetate ion, which acts as the base. Hco₃⁻ + h₂o → h₂co₃ + oh⁻. Now i didn't draw on lone pairs of electrons for. It becomes the hydrogen sulfite ion ( hso− 4 ) which is the. Web so on the right, this would be the conjugate base to acetic acid. A conjugate acid is formed when a proton is added to a base, and a conjugate base is formed when a proton is removed from an acid. For example, if you have a mixture of benzoic acid and propylbenzene: All acids have a conjugate base. All bases have a conjugate acid. Add a unit of negative charge to the molecule. Base + acid → conj a + conj b.
Chapter 10 Exercises 3 and 4 Drawing Conjugate Acids and Conjugate

How to typset/draw conjugate acids and bases

How to Identify Acid, Base, Conjugate Acid, and Conjugate Base Examples
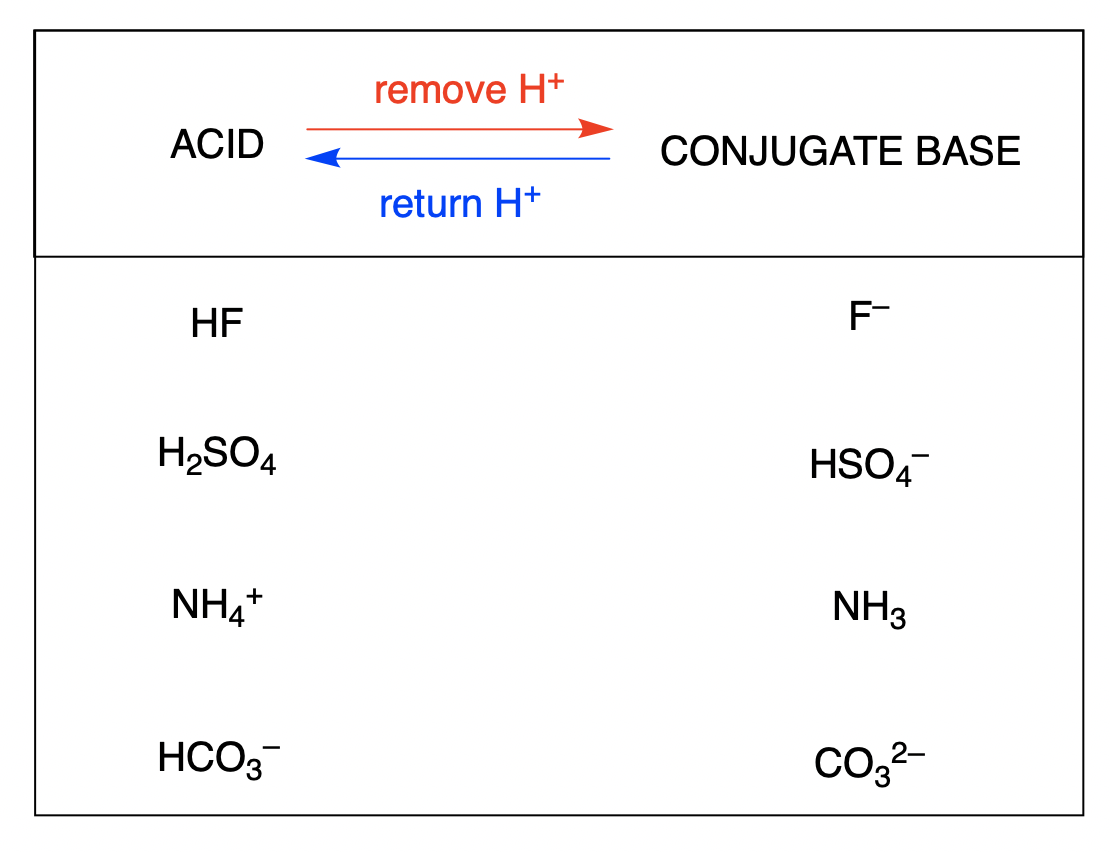
5.1 AcidBase Definitions & Conjugate AcidBase Pairs General
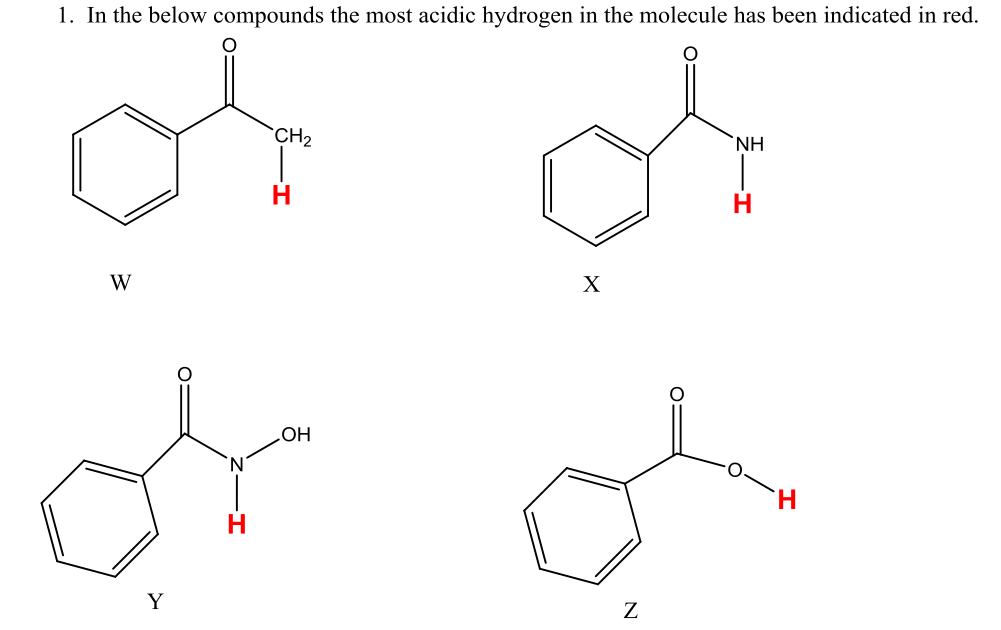
Solved A. Draw the conjugate base of each acid, including

Acids and Bases (Alevel) ChemistryStudent
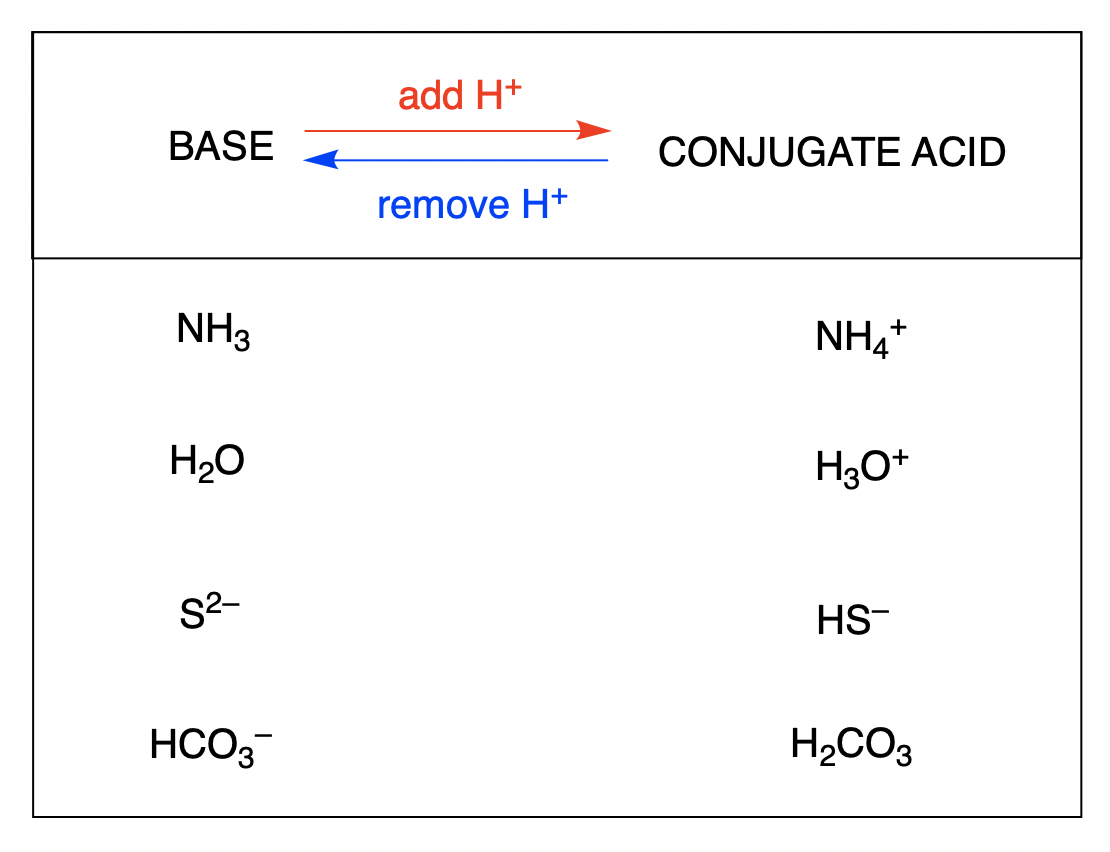
Enter the Conjugate Base for Each Acid.

CHEM112 5 6 drawing conjugate acids and bases YouTube
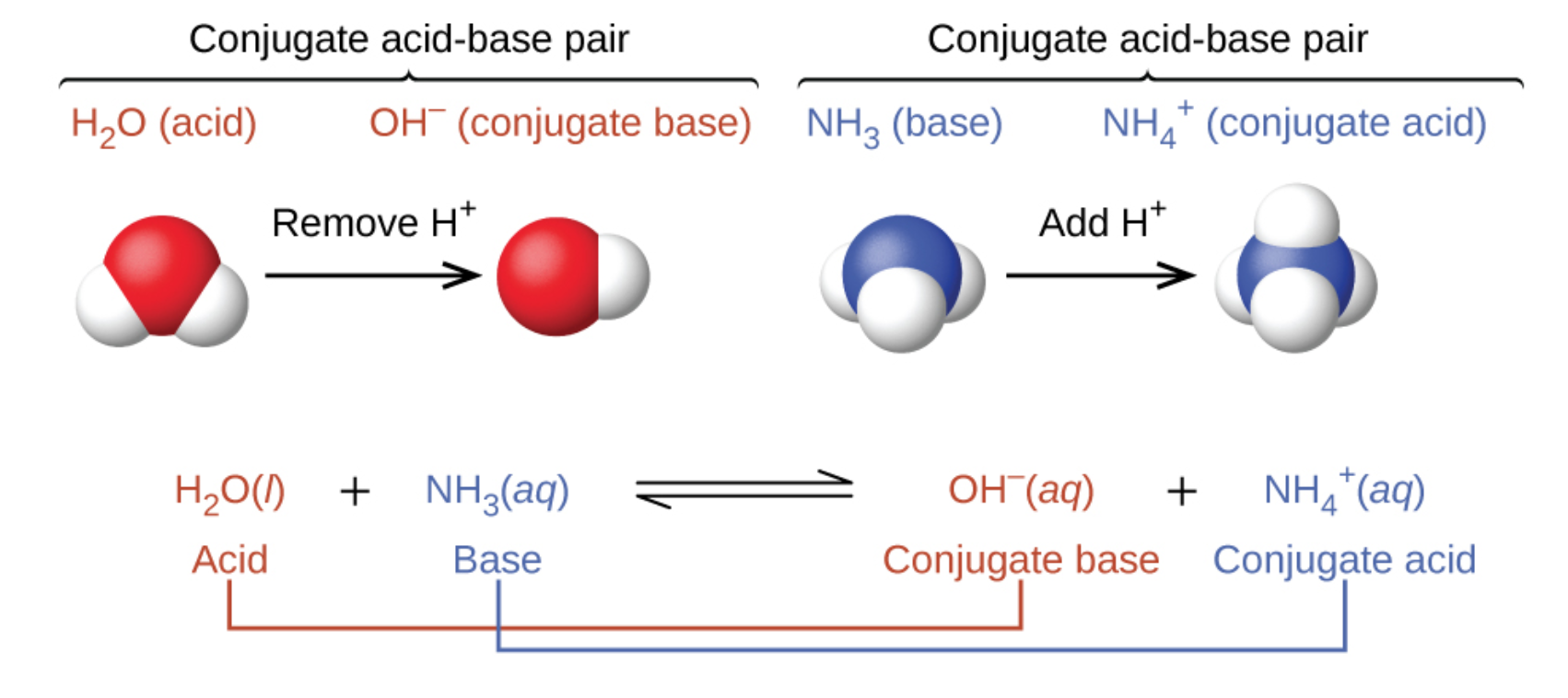
5.1 AcidBase Definitions & Conjugate AcidBase Pairs General

Conjugate AcidBase Pairs — Overview & Examples Expii
The Parent Acid And Its Conjugate Base (\(Ch_3Co_2H/Ch_3Co_2^−\)) And;
These Compounds Contain [Mostly Polar Bonds / Mostly Nonpolar Bonds].
Web View The Full Answer.
In This Example, Sulfuric Acid ( H2So4 ) Is An Acid Because It Donates H+ To The Water.
Related Post: