Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing
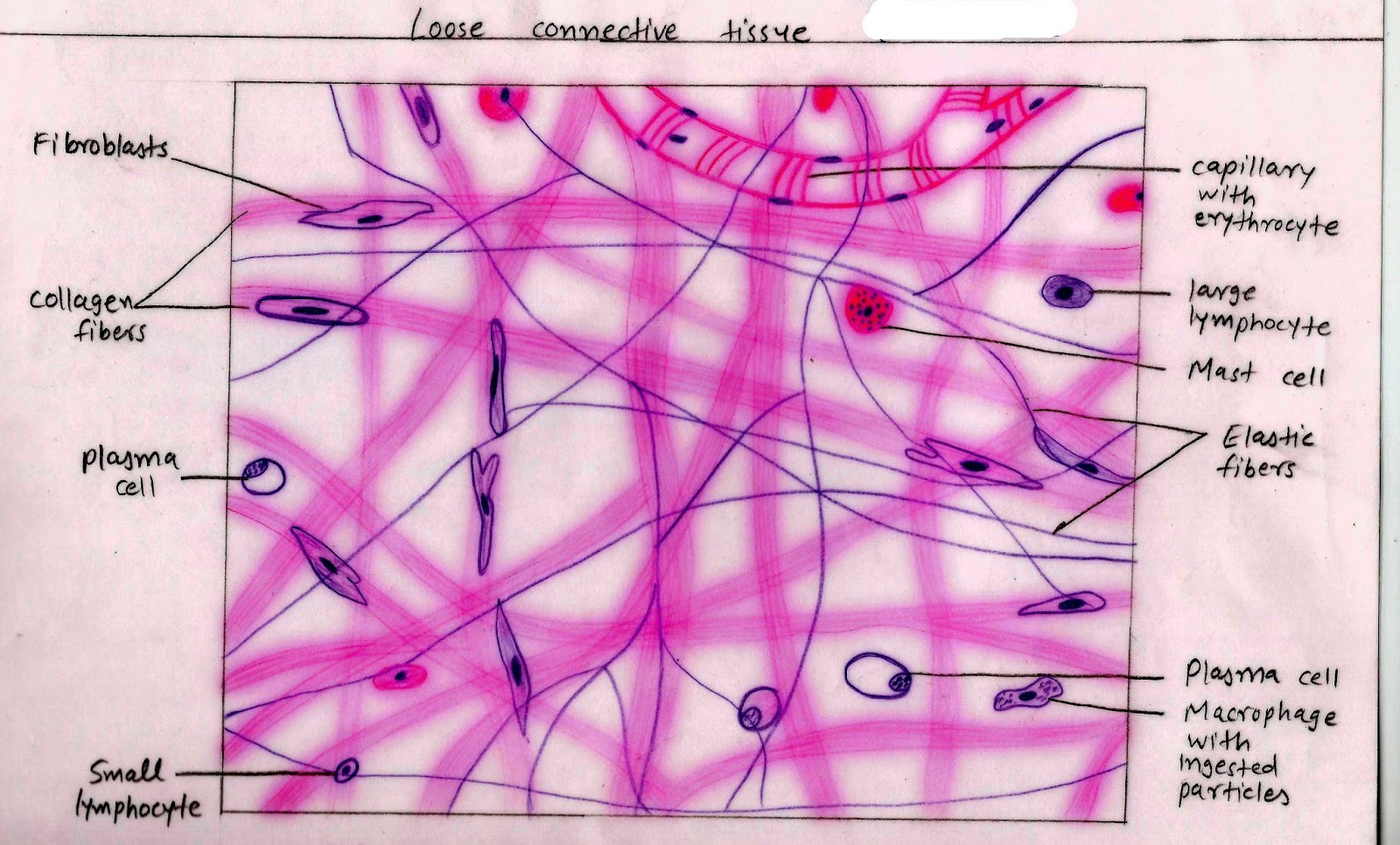
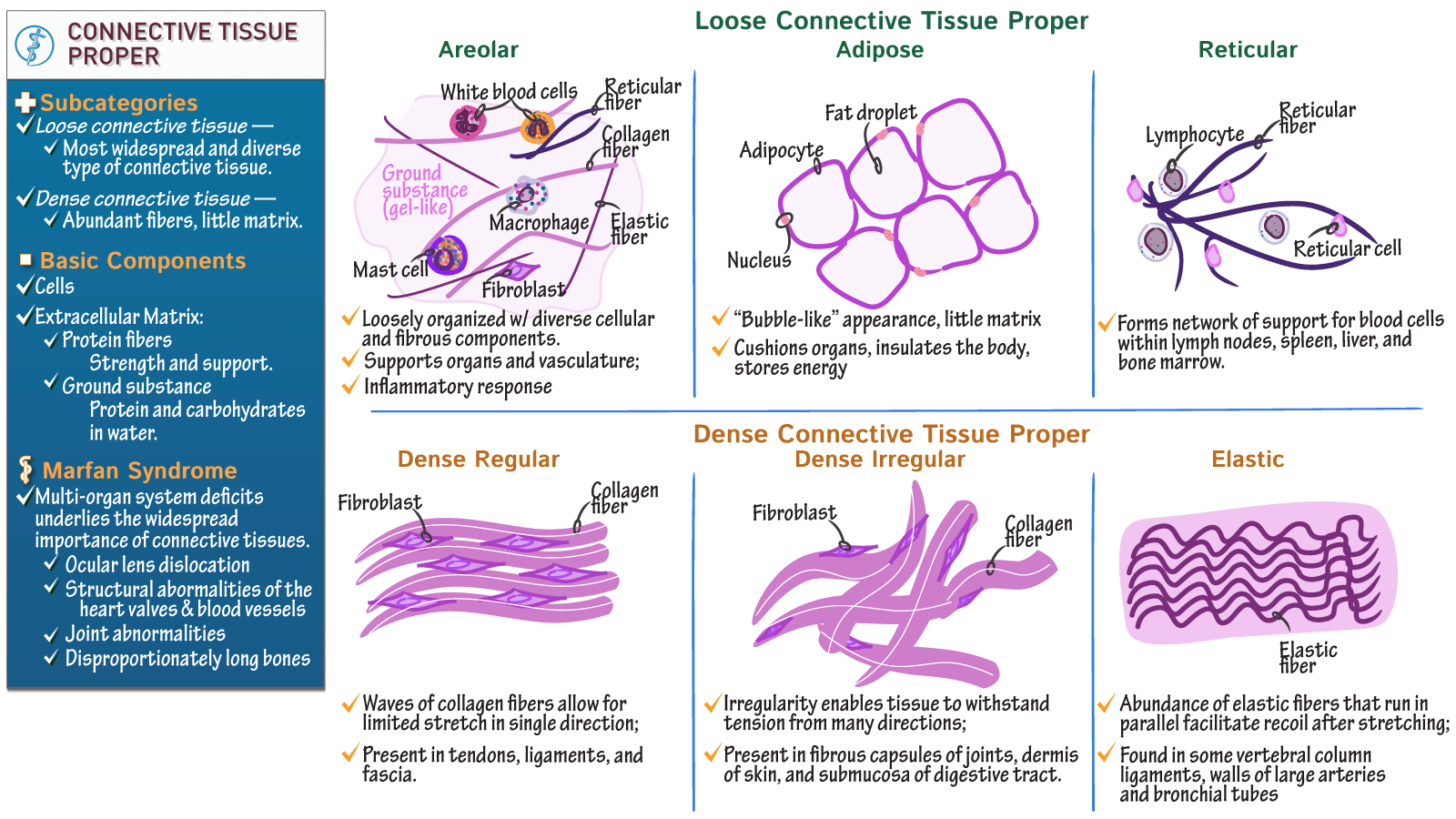
Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing - Please put total magnification in the image key. Web reticular tissue, a type of loose connective tissue in which reticular fibers are the most prominent fibrous component, forms the supporting framework of the lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils), bone marrow and liver. Web types of connective tissue: • compare the interrelationship of epithelial and connective tissue through a study of the skin. Web reticular tissue is a specific form of connective tissue predominating in several regions with high cellular content. The cells that make the reticular fibers are fibroblasts called reticular cells. Reticular tissue, a type of loose connective tissue in which reticular fibers are the most prominent fibrous component, forms the supporting framework of the lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils), bone marrow and liver. • study the characteristics of loose, dense, elastic, and reticular connective tissue, adipose tissue, cartilage, and bone. In this topic, we will explore the various aspects of reticular connective tissue drawing, including its structure, function, and importance. And that is going to be that reticular connective tissue forms the internal scaffolding for soft organs such as for example, the lymph nodes, the spleen, the liver, the kidneys, the thymus and the bone marrow, for example. If there is abundant space between protein fibers, the tissue is likely one of the loose connective tissues. Learn everything about it in the full version of this video:. Reticular fibers are not unique to reticular connective tissue, but only in this type they are dominant. Web reticular tissue is a type of connective tissue proper with an extracellular matrix. • study the characteristics of loose, dense, elastic, and reticular connective tissue, adipose tissue, cartilage, and bone. These fibers are actually type iii collagen fibrils. Web categorized under loose connective tissues, reticular connective tissues are also named as reticular fibers, which are an essential part of the body’s tissue framework. The units that together form these fibers are called reticular. Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix (ecm). The cells that make the reticular fibers are fibroblasts called reticular cells. Please put total magnification in the image key. The units that together form these fibers are called reticular cells or fibroblasts. Web reticular tissue is a special subtype of. Reticular connective tissue forms a scaffolding for other cells in several organs, such as lymph nodes and bone marrow. This layer is well vascularized and has a rich sensory and sympathetic nerve supply. These fibers are actually type iii collagen fibrils. Web types of connective tissue: Web reticular tissue is a special subtype of connective tissue that is indistinguishable during. Web reticular connective tissue is named for the reticular fibers which are the main structural part of the tissue. Reticular fibers are not unique to reticular connective tissue, but only in this type they are dominant. Fine fibers 1) connective tissue proper: Web connective tissue supports and protects · anatomy and physiology reticular connective tissue: None connective tissue is the. The cells that make the reticular fibers are fibroblasts called reticular cells. The units that together form these fibers are called reticular cells or fibroblasts. Look at various slides of the same tissues, some slides can give you a different perspective and reveal specific structures you may not have seen in other slides. Web here in this video, we're only. Reticular connective tissue is a type of connective tissue [1] with a network of reticular fibers, made of type iii collagen [2] ( reticulum = net or network). Please put total magnification in the image key. As you examine this photomicrograph, note that the reticular fibers may be found singly or in clumps. The major organs associated with this system. Web reticular tissue is a special subtype of connective tissue that is indistinguishable during routine histological staining. Web reticular tissue is a special type of connective tissue that predominates in various locations that have a high cellular content. • observe the characteristics of the three types of muscle Underlying the papillary layer is the much thicker reticular layer, composed of. Like all tissue types, it consists of cells surrounded by a compartment of fluid called the extracellular matrix (ecm). The major organs associated with this system are the bone marrow, intestines, kidney, spleen, and liver. Collagen, reticular, and elastic fibers. Web the res is composed of large populations of mononuclear phagocytes that associate with reticular connective tissue and act as. Underlying the papillary layer is the much thicker reticular layer, composed of dense, irregular connective tissue. These fibers are actually type iii collagen fibrils. Web the collagen and elastic fibers of connective tissue proper are histologically distinguishable as three fiber types: Fine fibers 1) connective tissue proper: Web categorized under loose connective tissues, reticular connective tissues are also named as. These fibers are made up of collagen and glycoproteins. Web reticular tissue is a type of connective tissue proper with an extracellular matrix consisting of an interwoven network of reticular fibers that provide a strong yet somewhat flexible framework (known as the stroma) for other types of functional cells to anchor within an organ or tissue. Web reticular connective tissue is named for the reticular fibers which are the main structural part of the tissue. These fibers are actually type iii collagen fibrils. If there is abundant space between protein fibers, the tissue is likely one of the loose connective tissues. Web the collagen and elastic fibers of connective tissue proper are histologically distinguishable as three fiber types: Collagen, reticular, and elastic fibers. Web here in this video, we're only going to focus on one main function of reticular connective tissue. Web the res is composed of large populations of mononuclear phagocytes that associate with reticular connective tissue and act as particulate filters. • observe the characteristics of the three types of muscle This layer is well vascularized and has a rich sensory and sympathetic nerve supply. As you examine this photomicrograph, note that the reticular fibers may be found singly or in clumps. • compare the interrelationship of epithelial and connective tissue through a study of the skin. They are nonelastic and have variable bundle thicknesses. Web reticular tissue, a type of loose connective tissue in which reticular fibers are the most prominent fibrous component, forms the supporting framework of the lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils), bone marrow and liver. In this topic, we will explore the various aspects of reticular connective tissue drawing, including its structure, function, and importance.
chapter 4 connective tissues neuron stuff and other science stuff

Reticular Connective Tissue Labeled

Reticular connective tissue Microscopic cells, Loose connective
Reticular Connective Tissue 20x Histology
Histology Image Connective tissue

Connective Tissue consists of reticular connective tissue and adipose

Connective Tissue Supports and Protects · Anatomy and Physiology

Reticular Connective Tissue Structure
BMS Anatomy Connective Tissue Proper ditki medical & biological sciences

Reticular Connective Tissue, 40X Histology
Web Connective Tissue Supports And Protects · Anatomy And Physiology Reticular Connective Tissue:
Like All Tissue Types, It Consists Of Cells Surrounded By A Compartment Of Fluid Called The Extracellular Matrix (Ecm).
The Cells That Make The Reticular Fibers Are Fibroblasts Called Reticular Cells.
Web Reticular Tissue Is A Special Subtype Of Connective Tissue That Is Indistinguishable During Routine Histological Staining.
Related Post: