The Drawing Shows Two Cars Traveling In Different Directions
The Drawing Shows Two Cars Traveling In Different Directions - Vbg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due north. I and carby are moving at 21 m/s. The velocity of car a relative to car b is vab. Car a is moving at 32.4 m/s due east. The ketcher v b g is directed to the norse and the a g is directed to the east. Web the drawing shows two cars traveling in different directions with different speeds. B if we find the relative velocity of a due to be. Which statement is true regarding the kinetic energies and momenta of the cars? Web the drawing shows two cars traveling in different directions with different speeds. Web the drawing shows two cars traveling in different directions with different speeds. Vag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 31.1 m/s, due east vbg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due north the driver of car b looks out the window and sees car a. Science physics theory of relativity. Vag = speed of car a. Web the drawing shows two cars. One is heading due east and the other due north, as the drawing shows. Web homework statement the drawing shows two cars traveling inbound different directions with different speeds. (a) they both have the same kinetic energies and the same momenta. Vag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 32.4 m/s, due east vbg = velocity of. (b) they have the same kinetic energies, but different momenta. Vag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 29.5 m/s, due eastvbg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due north the driver of car b looks out the window and sees car a. Web the drawing shows two cars travelling in. The velocity of car a relative to car b is vab. V a b will simply be v a minus v. (b) they have the same kinetic energies, but different momenta. B if we find the relative velocity of a due to be. Vbg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due north. The velocity of car a relative to car b is vab. Web the drawing shows two cars traveling in different directions with different speeds. Web the drawing shows two cars traveling in different directions with different speeds. Web the drawing shows two cars traveling in different directions with different speeds. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like. Web homework statement the drawing shows two driving traveling in different locator with different speeds. I and carby are moving at 21 m/s. (b) they have the same kinetic energies, but different momenta. Vag = velocity of car a relative at the ground = 27.0 m/s, just east vbg = rapidity of machine b relative to which ground = 21.0. B if we find the relative velocity of a due to be. Vag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 29.5 m/s, due eastvbg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due north the driver of car b looks out the window and sees car a. Vag = velocity of car a. (see picture) the drawing shows two cars traveling in different directions with different speeds. Vag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 32.4 m/s, due eastvbg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due norththe driver of car b looks out the window and sees car a. Web the drawing shows two. V a b will simply be v a minus v. Vag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 27.0 m/s, due east vag = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due north the passenger of car b looks out the window and sees car a. Vag = velocity of car a relative. The speed of the car relative to the ground is 30.2 meters per second and the speed of the car relative to the ground is 21 meters per second. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like two identical cars are traveling at the same speed. The ketcher v b g is directed to the norse and the. Web homework statement the plot shows two cars traveling in different directions with different max. Vag= velocity of car a relative to the ground = 31.3 m/s, due east vbg= velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due north the driver of car b looks out the window and sees car a. Vag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 31.2 m/s, due east vbg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due norththe driver of car b looks out the window and sees car a. One is heading due east and the other due north, as the drawing shows. Vbg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due north. Vag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 27.0 m/s, due east vag = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due north the passenger of car b looks out the window and sees car a. V ag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 33.9 m / s , due east v bg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m / s , due north the driver of car b looks out the window and sees car a what is the velocity (magnitude and. Car a is moving at 32.4 m/s due east. Web the drawing shows two cars traveling in different directions with different speeds. V a b will simply be v a minus v. Vag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 32.4 m/s, due eastvbg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due norththe driver of car b looks out the window and sees car a. Web homework statement the drawing shows two driving traveling in different locator with different speeds. Web homework statement the drawing shows two cars traveling inbound different directions with different speeds. Vag = drive of motor a. Vag = velocity of car a relative to the ground = 34.9 m/s, due east vbg = velocity of car b relative to the ground = 21.0 m/s, due north the driver of car b looks out the window and sees car a. Web focus on concepts, question 16 the drawing shows two cars traveling in different directions with different speeds.
Two Cars Running in Opposite Direction Stock Illustration
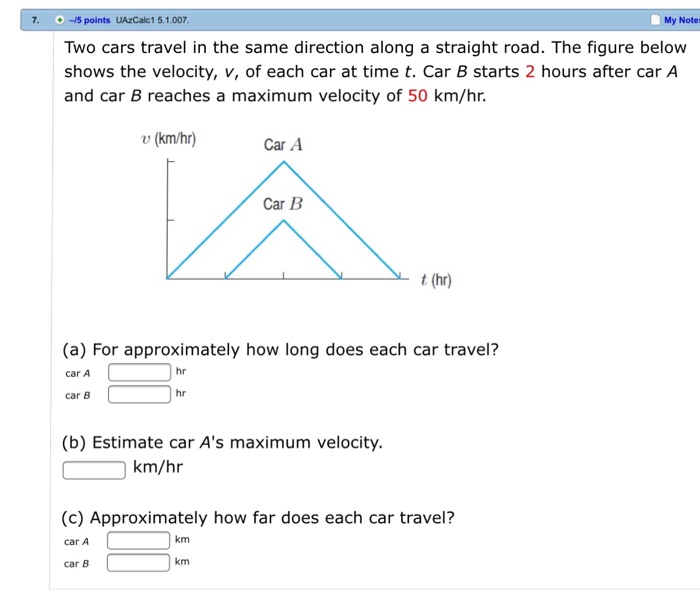
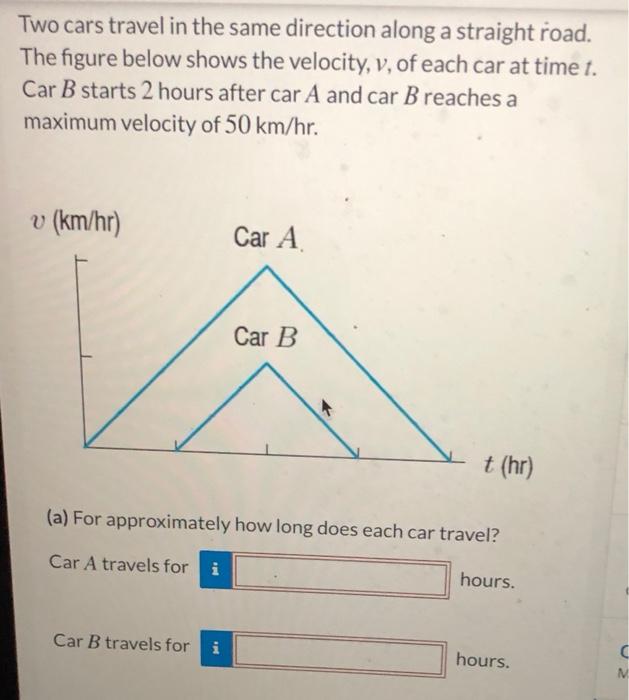
Solved Two cars travel in the same direction along a

Solved Two cars travel in the same direction along a
Solved Two cars travel in the same direction along a
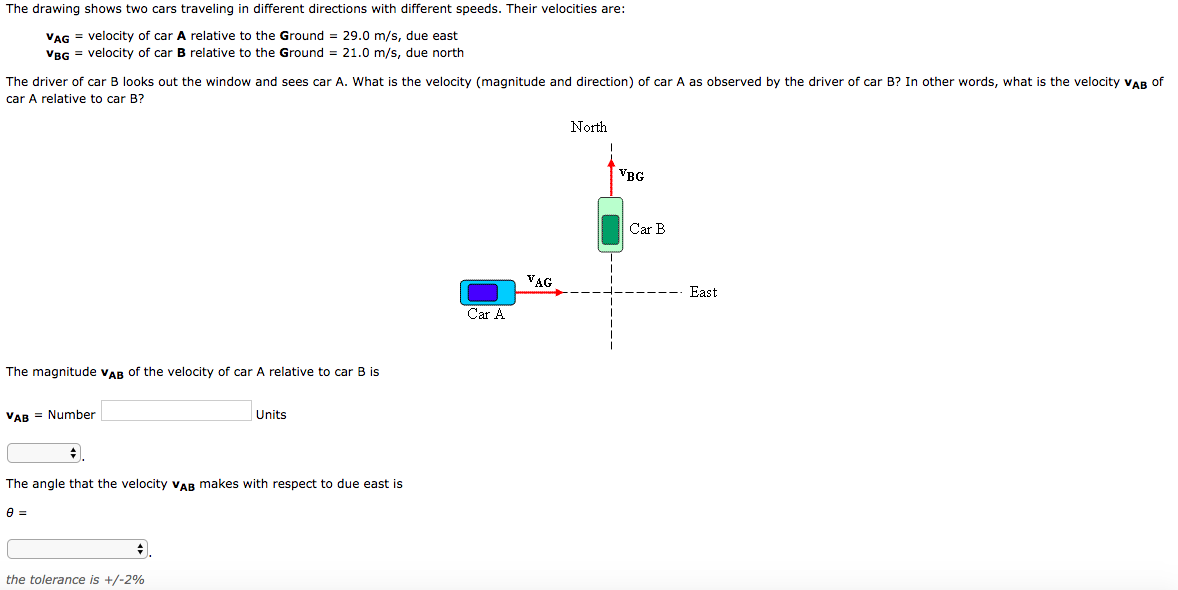
Solved The drawing shows two cars traveling in different
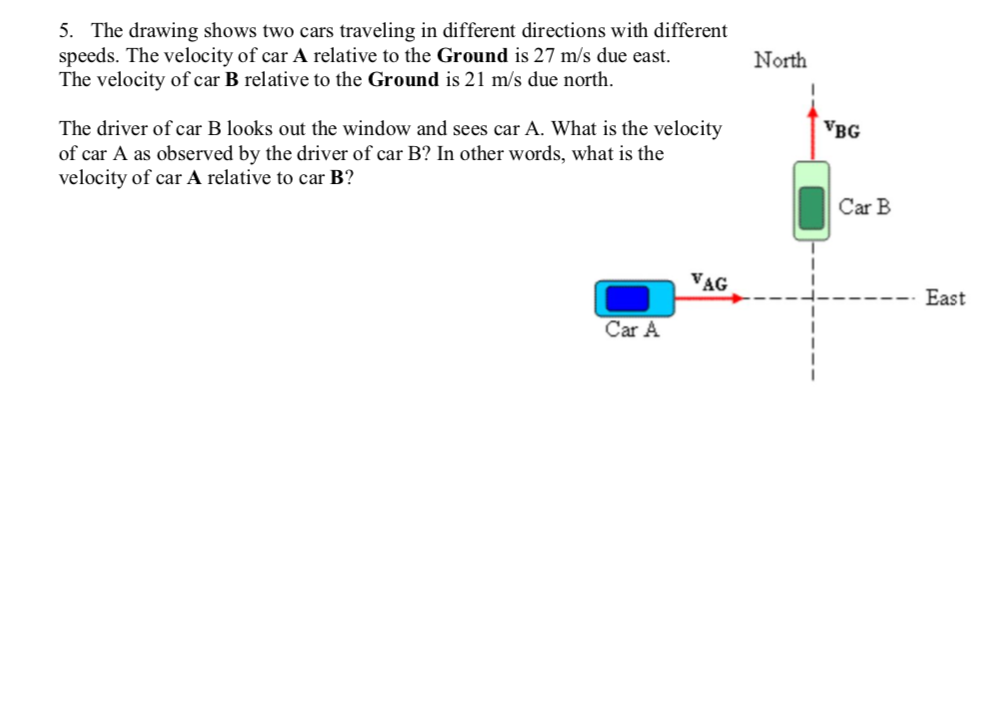
Solved 5. The drawing shows two cars traveling in different

Two cars are moving with same velocity of 30 km

Solved Two cars traveling with the velocities shown collide
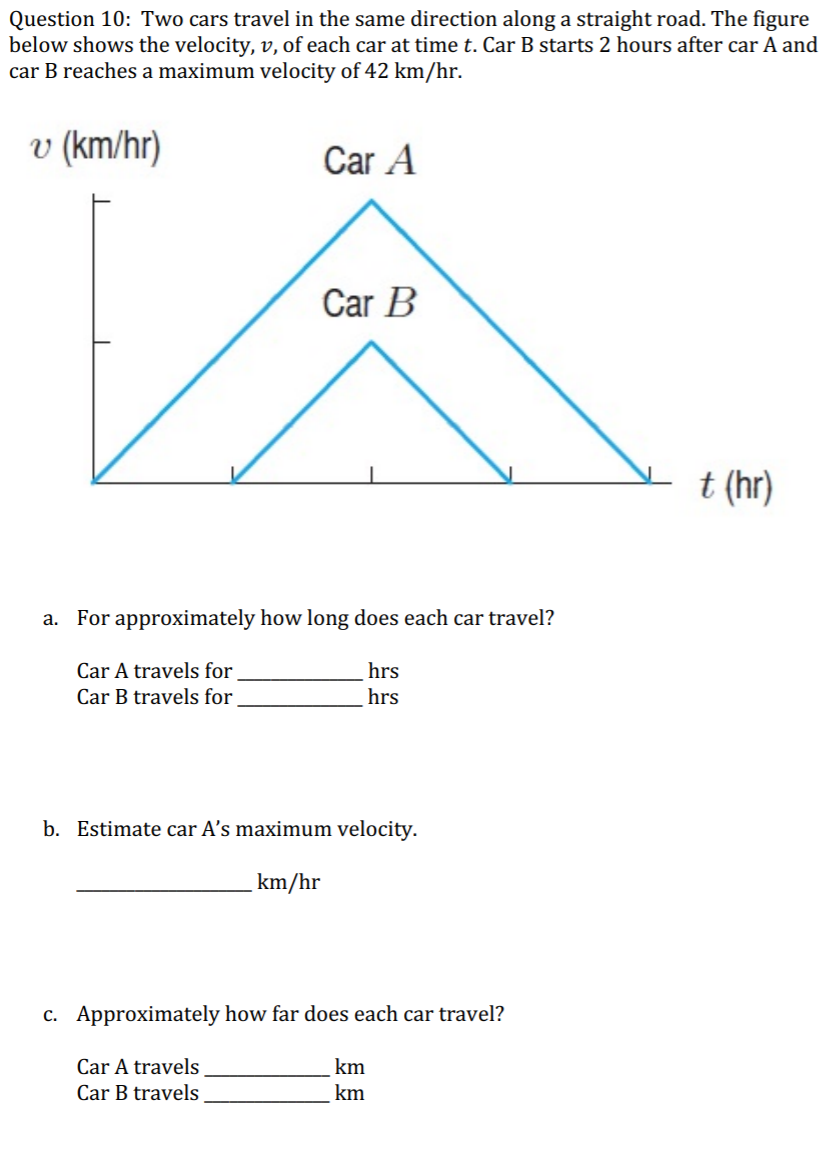
Solved Question 10 Two cars travel in the same direction
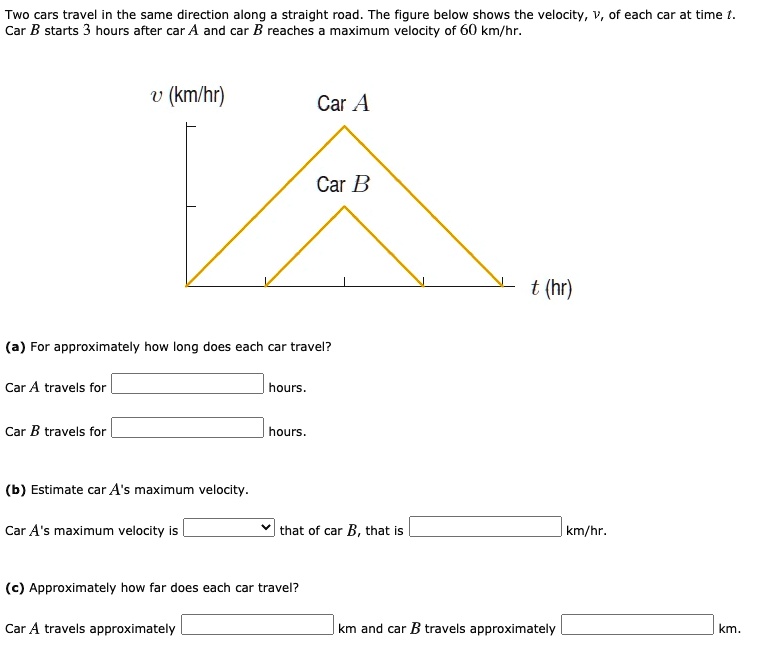
SOLVED Two cars travel in the same direction along straight road The
Vag = Velocity Of Car A Relative To The Ground = 31.1 M/S, Due East Vbg = Velocity Of Car B Relative To The Ground = 21.0 M/S, Due North The Driver Of Car B Looks Out The Window And Sees Car A.
Vag = Velocity Of Car A Relative To The Ground = 29.5 M/S, Due Eastvbg = Velocity Of Car B Relative To The Ground = 21.0 M/S, Due North The Driver Of Car B Looks Out The Window And Sees Car A.
The Speed Of The Car Relative To The Ground Is 30.2 Meters Per Second And The Speed Of The Car Relative To The Ground Is 21 Meters Per Second.
Web The Drawing Shows Two Cars Traveling In Different Directions With Different Speeds.
Related Post: